Digitalization of the wind sector
The digitalisation of the wind energy sector, advances and opportunities
Energy efficiency Offshore wind Onshore wind
La digitalización en el sector eólico está suponiendo todo un avance a la hora de reducir costes, mejorar los rendimientos y la seguridad, así como tomar decisiones de una manera más eficiente. Aunque aún queda recorrido, especialmente en lo que se refiere a la medición y el intercambio de datos.

As in other sectors, digitalisation has been a revolution in the world of wind energy. Not only has it contributed to the enormous development of wind energy, but it has also made this growth increasingly more efficient, safer and more profitable. Digitalisation, for example, helps to reduce operation and maintenance costs - the so-called O&M - while improving performance and productivity, ultimately making wind a much more competitive source of energy.
Given the growth forecast for wind energy - global installed wind capacity is expected to more than double in the next decade - and the importance of this development in achieving climate neutrality targets by 2050, there is a need to go one step further and continue to innovate in digitalisation.
This is precisely the subject of one of the latest reports by WindEurope, the European wind energy agency, titled 'Wind energy digitalisation towards 2030', which analyses the state of digitalisation in the wind energy sector, investigates the role played by the data collected and considers the expected evolution of the various digital applications and technologies towards 2030.
This drive requires, for example, the establishment of common terminology and metrics to measure, collect and transmit a range of operational data, allowing standardisation in the comparison and analysis of information. This simplifies the comparison of the potential benefits of digital applications.
In this way, by developing reliable universal metrics, technologies can not only be more properly validated, but also more easily made transferable at lower cost, thanks to well-established data exchange systems within the organisations themselves.

Innovation in renewables
We innovate to improve the efficiency of our renewable assets.

MeteoFlow Project
Anticipating weather events to optimise renewable production.

Digitalisation in renewable energy
Why is it crucial for the future of energy systems?
Blockchain in the energy market
How can blockchain be used to certify the source of green energy?
Iberdrola's pioneering initiatives in digitalisation
Iberdrola posee varios proyectos de éxito en materia de digitalización que han sido seleccionados como ejemplo a nivel europeo por WindEurope y así lo ha reseñado la organización en el informe 'Wind energy digitalisation towards 2030'. Uno de ellos es Meteoflow big data que, como su nombre indica, hace referencia al uso de big data así como técnicas de Inteligencia Artificial y técnicas de machine learning para generar modelos de predicción que tengan en cuenta todos los parámetros meteorológicos, incluso a decenas de kilómetros, que puedan influir en un parque eólico. Estos modelos de predicción combinan por una parte modelos meteorológicos globales de matrices tridimensionales con datos de condiciones climáticas obtenidos de los propios parques, así como con el histórico de rendimiento.
Iberdrola has several successful digitalisation projects that have been selected as examples at European level by WindEurope, as highlighted by the organisation in the report 'Wind energy digitalisation towards 2030'. One of them is Meteoflow big data which, as its name suggests, refers to the use of big data as well as Artificial Intelligence and machine learning techniques to generate prediction models that take into account all meteorological parameters, even from tens of kilometres away, that can influence a wind farm. These prediction models combine, on the one hand, global meteorological models of three-dimensional matrices with data on climatic conditions obtained from the wind farms themselves, as well as historical performance.
This results in more reliable predictions, but also requires more data storage capacity and significant post-processing of the data obtained. This is currently the most important challenge.
How MeteoFlow has evolved with big data
The statistical models used by MeteoFlow in its forecasts are fed with:
-
Historical production data
-
Weather forecast data from multiple sources
MeteoFlow with big data
- More than 10,000 information points are selected
- 1 Selection of information samples.
- 2 Data management and optimisation in a big data environment.
- 3 Selection of most influential points in prediction.

- The wind estimate was taken at 1 or 2 points on the vertical of a given installation.

Upgrades
-
Much more accurate weather forecasting
-
Increased use of renewable resources
-
Maximising the supply of clean energy on the grid
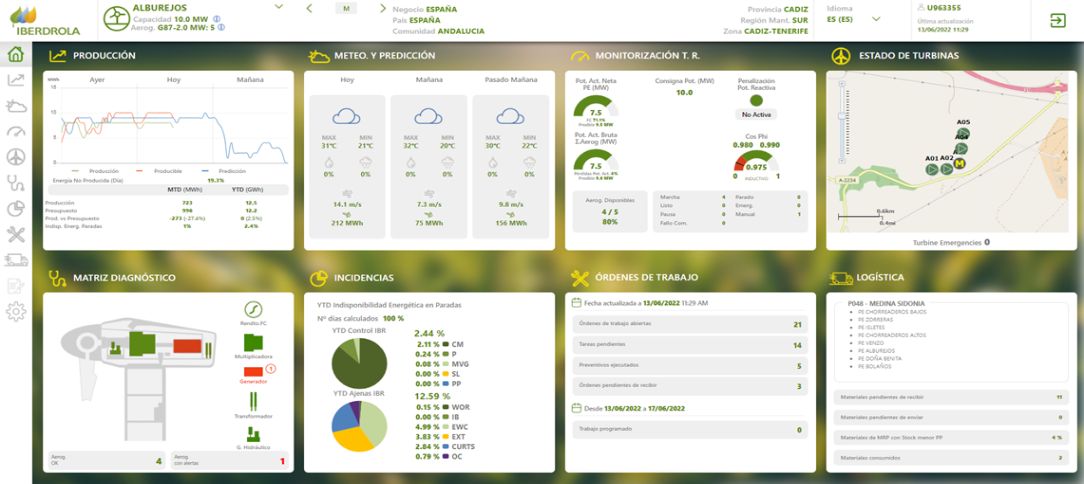
Another digitalisation initiative carried out at Iberdrola is the development of the Asset Dashboard. This tool provides real-time information on the key indicators (KPIs) for proper management of the maintenance of the company's renewable assets. Having information on the production, producibility and predictability of the asset that you maintain gives field personnel a very favourable position for making decisions aimed at maximising operational efficiency.
This application also allows you to know in real time the availability value, the maintenance work that is active, those that are still pending, any operational alerts that may exist, weather alerts as well as the stock of materials in the warehouse.