Energy efficiency in buildings
Eight steps towards sustainable construction
Sustainable architecture promotes efficient energy use in buildings in order to prevent unnecessary energy costs, to take advantage of local resources for system operations, and to ensure that there are no negative environmental impacts. Iberdrola is part of the Madrid World Capital of Construction, Engineering and Architecture Association (MWCC), as the leading exponent of the energy transition, contributing its experience and technical capacity to consolidate the association's project at national and international level.
Here are some examples:
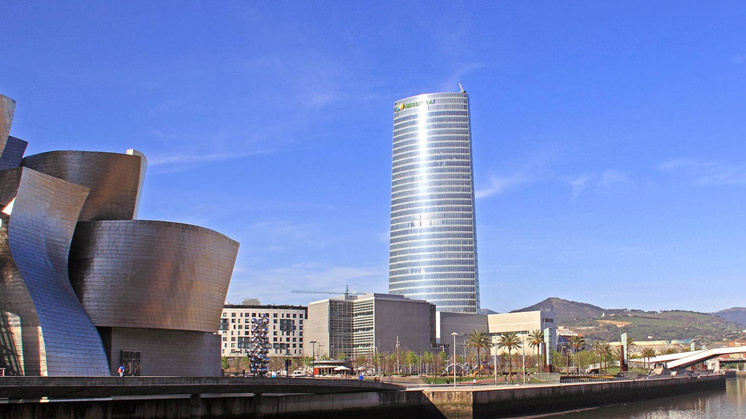
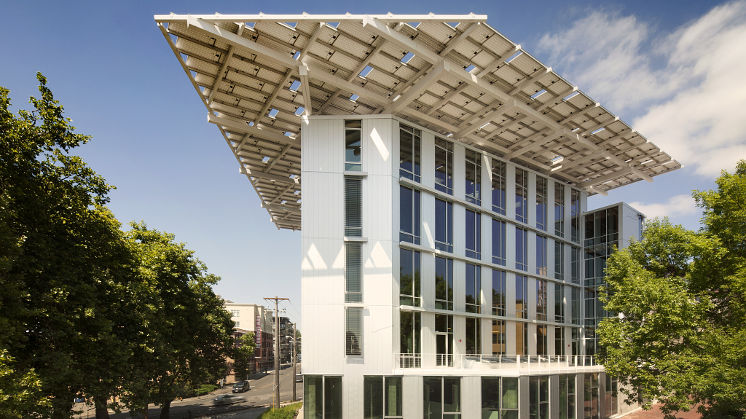
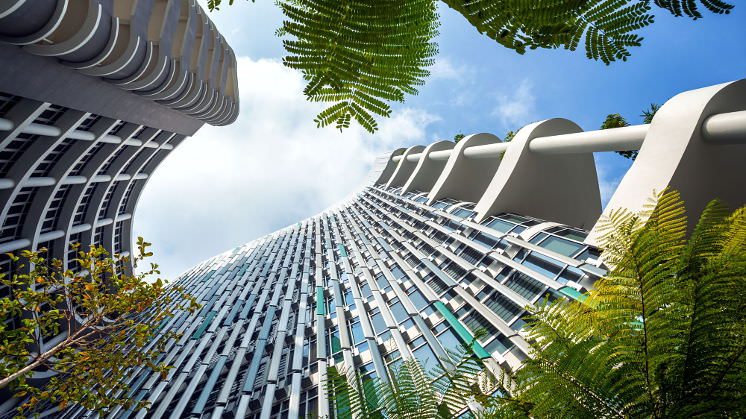




Innovative construction methods, new materials, and technological advances are boosting the energy efficiency of new buildings worldwide. Housing that saves 75% on heating costs, hospitals that consume 70% less energy, shopping centres that barely waste any water... How is this possible?
The key lies in the design. First, the design is aligned with nature by choosing the appropriate location and orientation of the structure to take advantage of sunshine for lighting and the breeze for cooling. Construction materials are increasingly recycled and are purchased from local suppliers to reduce the carbon footprint from shipping. Likewise, proper insulation is used to reduce the need for heating and air conditioning as much as possible.
New technologies are essential throughout this entire process: evaporative cooling towers, water recycling systems, solar panels, smart temperature and humidity management, etc. Additionally, sustainable buildings encourage a lifestyle that protects the environment: bike parking, vertical gardens, and rainwater catchment and treatment. All of these elements demonstrate how architecture can help in the fight against climate change.
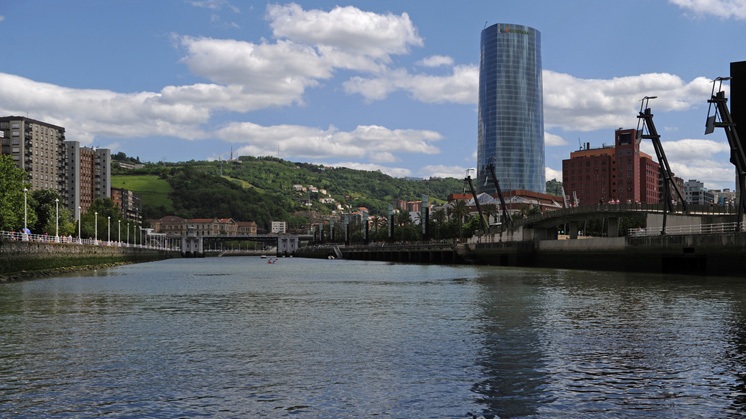

Iberdrola Tower, the energy of an idea. Video voice transcription (Spanish version) [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
Certified sustainability
Many organisations have developed seals of excellence over the last 25 years to push the trend towards sustainable construction, promoting innovation, and energy efficiency: LEED External link, opens in new window., BREEAM
External link, opens in new window., BREEAM External link, opens in new window., Passive House
External link, opens in new window., Passive House External link, opens in new window. or Living Building Challenge are some of the most prevalent ones. Companies, public bodies, and architecture firms around the world compete for certification.
External link, opens in new window. or Living Building Challenge are some of the most prevalent ones. Companies, public bodies, and architecture firms around the world compete for certification.
How is building sustainability measured?
The LEED certification, awarded by the Green Building Council in the United States, scores 8 prerequisites needed for sustainable construction:
Location and transportation
- Avoid building in natural environments
- Reduce the duration of car trips
- Encourage public transit and physical activity
Sustainable sites
- Protect or restore the local habitat
- Revitalize abandoned areas
Responsible waste management
- Efficient re-use
- Irrigation system control
- Moderate consumption
Energy and air quality
- Demonstrate a percentage of energy savings
- Use clean, renewable energy
Materials and inputs
- Recycled, renewable, or Green Seal-certified materials
Interior air quality
- Ventilation
- Temperature and acoustic comfort
- Proper lighting
100 points

Design innovation
- Proposals for new conservation strategies
Regional priority
- Attend to local environmental issues
10 points
LEED Certifications
-
Certified 40-49 points
-
Silver 50-59 points
-
Gold 70-79 points
-
Platinum More than 80 points

Iberdrola Tower
Symbol of our commitment to innovation, sustainability and art

Sustainable management
We are an international benchmark for sustainability