Digital divide
Digital divide throughout the world and why it causes inequality
ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) offer many advantages: greater access to information, cost reduction in the labour sector, greater connectivity between people, etc. However, digitalisation is not happening equally all over the world, because imbalance exists and this is known as the digital divide.

In 2020 our lives changed completely when COVID-19 locked us in our homes for months and forced us to study, work and see each other through a screen. Years later, the online format and working from home are here to stay, with more and more companies opting for this option in combination with face-to-face to carry out their business. However, not everyone has the same opportunities to be connected. According to a study by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), a specialised agency of the United Nations (UN), 33% of the world's population - 2.6 billion people - have no access to the internet or have never used it.
What is the digital divide?
Inequality in access to the Internet and ICT is known as the digital divide. In 2023, 70% of men used the internet, compared to 65% of women. Some 17% more women worldwide are offline than men, according to the ITU report.
This gap becomes even wider when we talk about regions: in January 2024, in India only 47.6% of its inhabitants didn’t have Internet access, compared to 10 % of Europeans and Americans.
The data shows the technological gap that separates some countries from others, despite the fact that 3G and 4G networks, while awaiting the massive expansion of 5G, are already reaching almost every corner of the planet. Here, it is important to distinguish between access to the Internet and digital literacy, that is, the learning process that enables a person to acquire the skills to understand and benefit from the educational, economic and social potential of the new technologies.
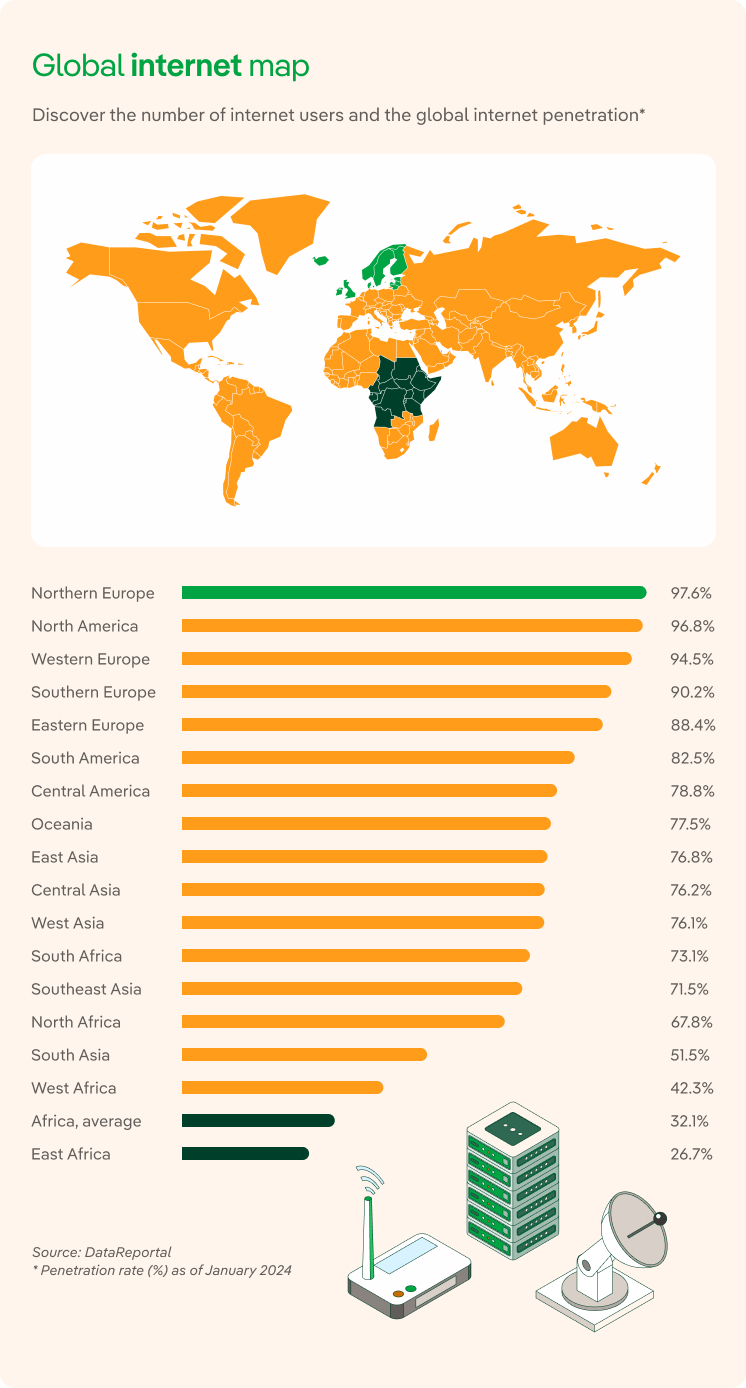
 SEE INFOGRAPHIC: The Internet world map [PDF]
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: The Internet world map [PDF]
Causes and types of digital divide
The digital divide was initially attributed to underdevelopment and was perceived as something temporary that would disappear with the popularisation of technology. Instead, the divide persists today despite the mass marketing of electronic devices with Internet access. The causes can range from the high price of the above-mentioned devices to the lack of knowledge about their use or the lack of infrastructure for their access. In this regard, we review the types of digital divide:
- Access divide. It refers to the possibilities that people have to access this resource. This is where socio-economic differences between people and between countries come into play, since digitisation requires very costly investments and infrastructure for less developed regions and for rural areas.
- Use divide. It refers to the lack of digital skills, which impedes the handling of technology. In this regard, and to give an example, the ITU points out that there are 40 countries in which more than half of their inhabitants do not know how to attach a file to an email.
- Quality of use gap. Sometimes they have the digital skills to find their way around the Internet, but not the knowledge to make good use of and get the most out of it. For example, with regard to access to quality information.
A few years ago, ITU established the Digital Access Index (DAI), which measures the overall ability of a country's citizens to access and use ICT. This index takes into account various variables grouped around five categories, which are as follows: quality, infrastructure, knowledge, accessibility and use.
Consequences of the digital divide
Technological discrimination is a form of poverty and social exclusion, depriving some citizens of essential resources for development and wealth generation. We saw this a lot during the COVID-19 pandemic, as many students and workers found it difficult to work from home and follow classes online. We review the main effects of the digital divide below:

Edadismo: la ONU señala la discriminación por edad como un problema a nivel mundial
Una de cada dos personas en el mundo tiene actitudes discriminatorias hacia los mayores.

'Blended learning', ¿cómo funciona el aprendizaje semipresencial?
El blended learning es un tipo de aprendizaje que combina la enseñanza en remoto y la presencial.

Entendiendo y aprovechando la diversidad generacional en el trabajo
La “diversidad generacional” es la presencia de diferentes grupos de edad dentro de una población, comunidad u organización.
Strategies on bridging the digital divide
The UN includes the reduction of the digital divide (SDG 9) in its Sustainable Development Goals. That is why, in many places initiatives have been launched to facilitate access to technology. Here we mention some of the most relevant ones:
- Digital literacy programs. They instruct people in less-favoured areas of Internet use to improve their personal well-being.
- Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI). This project, led by an international coalition of governments, businesses and civil society, aims to lower the cost of broadband in specific areas in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
- Free Basics. This initiative, promoted by Facebook and six other technology companies, aims to provide free access to a number of websites through a mobile application.
- Starlink. This project, promoted by tycoon Elon Musk, is launching satellites into space to provide high-speed Internet and global coverage at affordable prices.
-
SheCodes Foundation. This project in Ghana aims to teach 2,000 women to write code and handle Artificial intelligence (AI) tools completely free of charge. There are currently 1,454 women enrolled in the initiative. Similar projects to bridge the digital divide have also emerged in other countries like Peru and Spain.
-
The European Union's DigComp framework. In the update to this document, the EU sets out 250 examples of knowledge, skills and attitudes to help citizens interact confidently and securely with digital technologies, and new and emerging technologies such as IoT.