Everything about 5G
5G! Welcome to the era of hyper-connectivity!
When people talk about the connected society, the thousands of possibilities offered by new technologies and our future lives in smart cities, a constellation of ultrafast devices springs to mind. A supporting infrastructure is required for all this to happen, which is where 5G comes in.

What is 5G and how does it work?
The hyper-connectivity of the immediate future is on the horizon: Internet of Things (IoT) apps, services for smart cities, unbelievable quantities of data... That's why apps and devices and, at the same time, the infrastructures to support them, are a pressing need. Speeds of 4G networks are not enough, hence the emergence of 5G, a technology that will transform smart devices into ultra-smart devices.
5G is the fifth generation of technologies and standards for wireless communication; i.e. the network used by mobile devices to connect to the Internet anywhere. It is an evolution of 4G that will revolutionise telecommunications and take us into a new world - hyperconnectivity. The millisecond latencies — the time it takes to transfer a data packet over the network — provided by 5G are essential to this.
The 5G, as seen in the last Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona, is an increasingly closer reality and, thanks to the minimum latency metioned, will facilitate:
- The first expansionary phase of real-time interconnected devices — from household appliances and gadgets to machinery, vehicles and every kind of sensor.
- A reduction, for example, in lag and signal dropout in streaming and online gaming.
- Lower energy consumption and longer battery life — up to 10% — in line with the current trend of achieving more with less in a sustainable economy.
Consultancy firm Gartner expects there to be 20,800 million devices connected by 2020. We are talking about any type of object that can send and receive useful information: smart meters, security devices, vehicle sensors, chips in clothing, etc. The consequence of this new paradigm is the appearance of new economic scenarios, business opportunities and business actors.
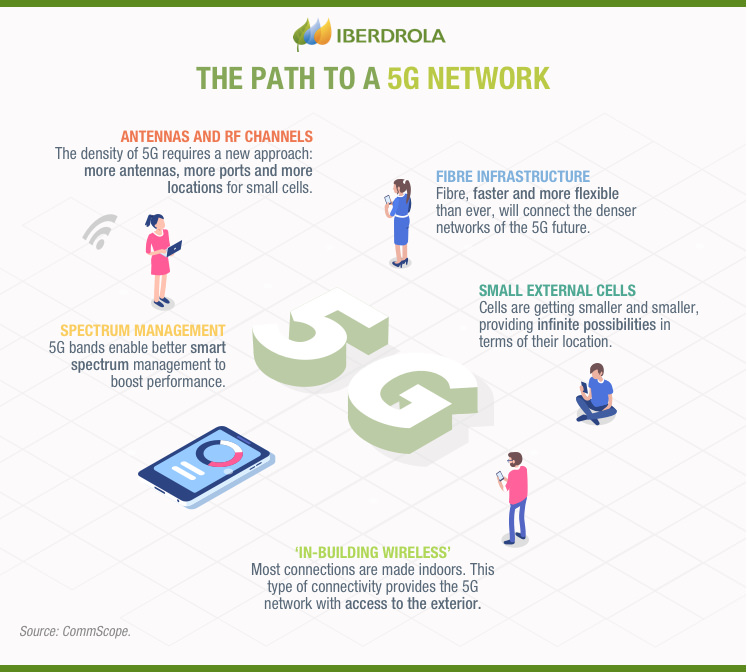
Discover the path to a 5G network
Antennas and RF channels
The density of 5G requires a new approach: more antennas, more ports and more locations for small cells.
Fibre infraestructure
Fibre, faster and more flexible than ever, will connect the denser networks of the 5G future.
Small external cells
Cells are getting smaller and smaller, providing infinite possibilities in terms of their location.
Spectrum management
5G bands enable better smart spectrum management to boost performance.
'In-building wireless'
Most connections are made indoors. This type of connectivity provides the 5G network with access to the exterior.
Hide information
The sectors that will benefit most from 5G
Consultancy firm McKinsey says that 5G will generate business worth 11 billion dollars by 2025. The combination of factors associated with new technology - increased productivity, cost savings and the appearance of disruptive solutions, will light the way for new businesses. For example, the agri-food industry is already working to improve crop sustainability by means of remotely monitored sensors.
There is a promising niche for smart city services, from traffic control to environmental data management. Then there's the wearables industry, with sports equipment and pharmaceutical products capable of performing diagnostics. New networks will also support the leap forward in communication, with 3D video and holographic calling. It sounds like science fiction, but the truth is that it's just around the corner.
The advantages of 5G by sectors
According to the document 5G Empowering Vertical Industries published by international consortium 5G PPP, new devices and services will benefit a number of strategic sectors:
Manufacturing
New production and organisational models based on information exchanged between connected objects.
Automotive industry
Autonomous and cooperative vehicles. The minimal latency will put safe autonomous vehicles on the roads.
Energy supply
Smart networks for far more efficient, sustainable distribution to industries and homes.
Entertainment and media
User-generated content. A total of 75% of mobile traffic will be in video format. Higher technical and touch-sensitive interfaces.
E-health and M-Health
Personalised services. Virtual hospitals and health centres. Remote surgery performed by robots.
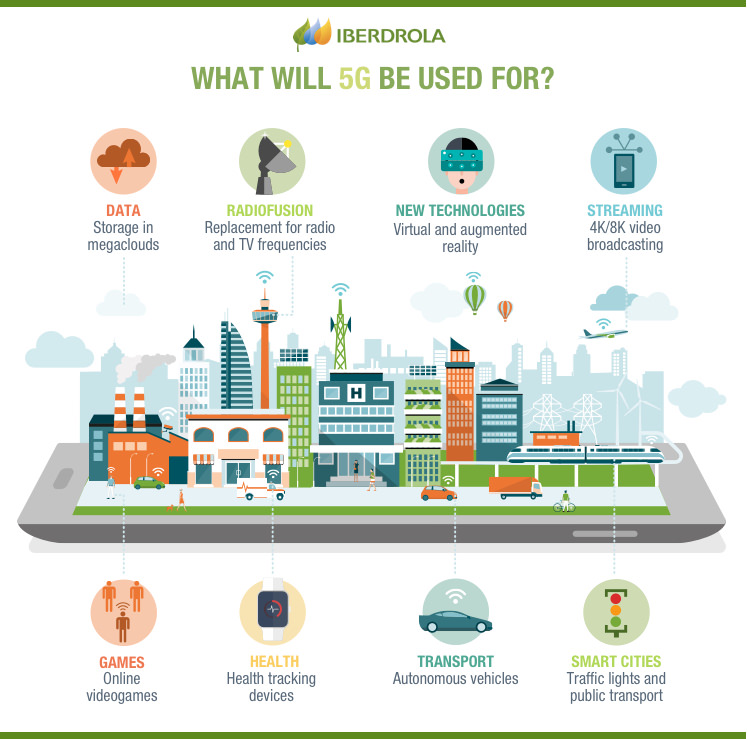
SEE INFOGAPHIC: What will 5G be used for? [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
Network development
The connectivity that makes mobile communication possible has been developed through several generations. Here's a summary of how we got to where we are today:
- 1G (1983): This allowed mobile-to-mobile calls.

- 2G (1991): The innovation was SMS messages.

- 3G (1998): Internet browsing became available.

- 4G (2008): It was now possible to send videos.

- 5G (2020): This will support the Internet of Things and sending of HD videos.

Digital twins - the keys to the Fourth Industrial Revolution
LiFi, the internet at the speed of light




