Excess renewable energy
When non-dispatchable renewable generation (photovoltaic or wind, which must be consumed when generated) exceeds electrical demand, the pumped-storage plant begins operating to make use of that surplus energy.
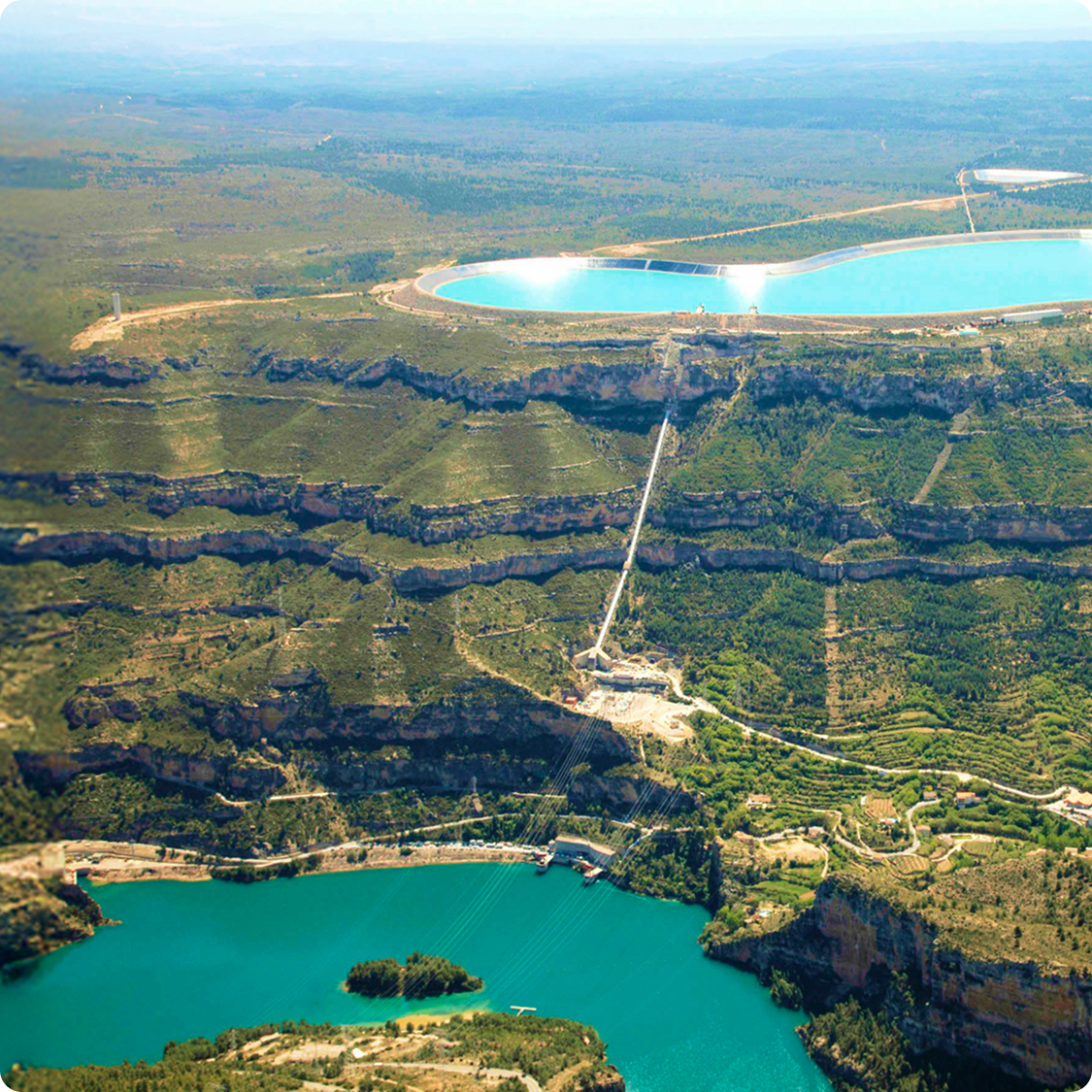

Their main purpose is to store water during periods of low demand and use it to generate energy during peak consumption hours. The largest pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant in Europe is La Muela II, commissioned by Iberdrola on the River Júcar, in the municipality of Cortes de Pallás in Valencia, with a pumping capacity of 1,316.8 MW. What’s more, in 2024 Iberdrola completed construction of the Tâmega Hydroelectric Complex in northern Portugal, with a generation capacity of 1,158 MW and a pumping capacity of 866 MW.
Pumped-storage hydroelectric technology is currently the most efficient system for storing energy on a large scale. It is the most cost-effective and provides stability, safety and sustainability to the electricity system, generating large amounts of energy with a very fast response time and without creating any kind of atmospheric emissions.
But first, what is energy storage? It is the capture and retention of energy for its later release and use – a key process in the energy transition from a fossil fuel-based system to an electricity model driven by clean energy. To achieve this, we rely on large-scale storage, such as the aforementioned pumped-storage hydroelectric power plants, and small-scale storage, through lithium-ion cells or batteries, which are key technologies for making electricity markets more flexible.
Focusing specifically on pumping systems, Iberdrola is a leader in energy storage with 4.2 GW of installed capacity using this type of technology. It is the most efficient energy storage method available today, as it produces no polluting emissions into the atmosphere and achieves a performance level far higher than the best batteries on the market.

Pumped-storage hydroelectric power plants have two reservoirs at different elevations that allow water to be stored by taking advantage of periods when energy demand is lower than renewable generation. Click on each of the headings below to find out how this type of facility operates:

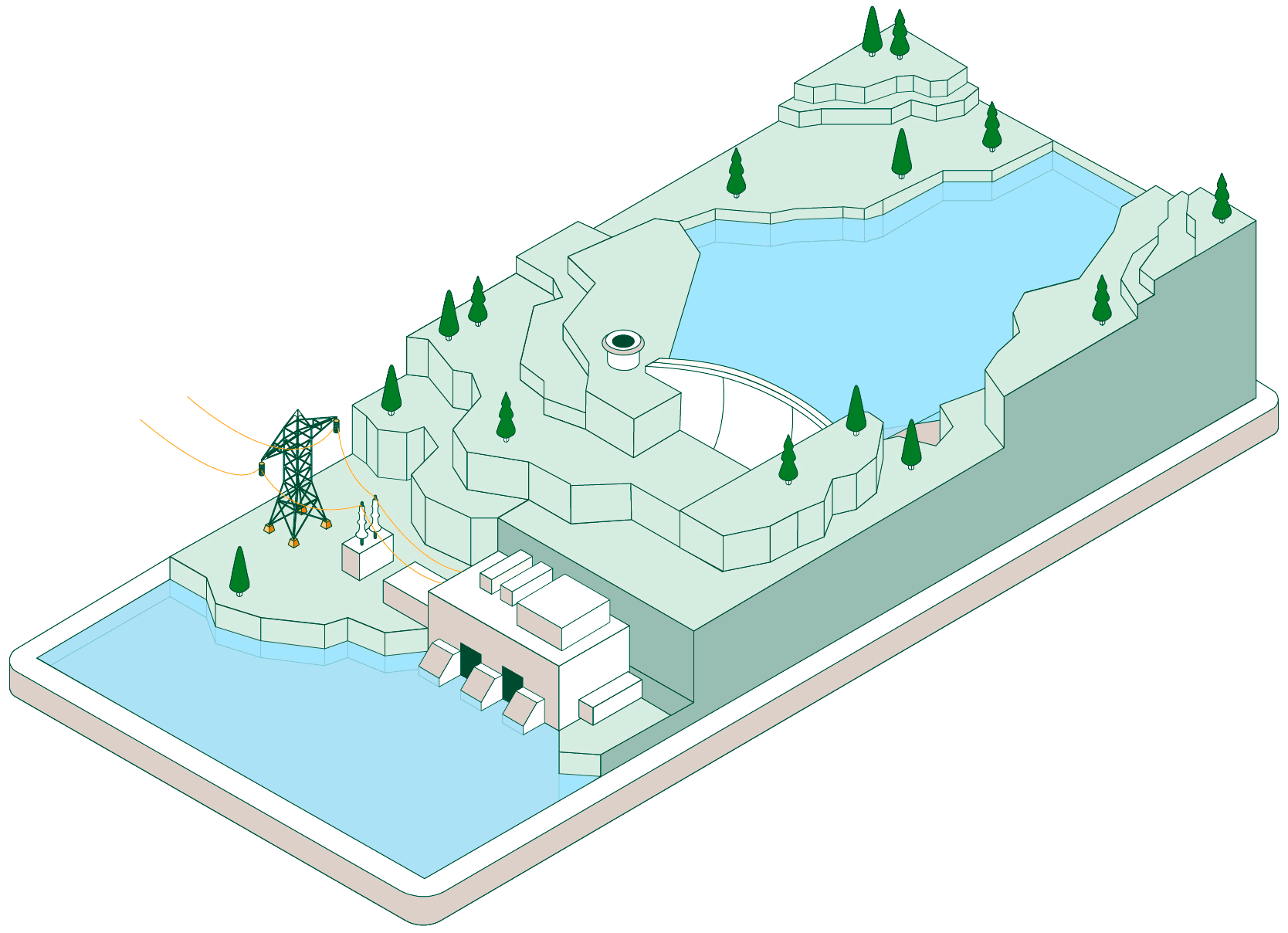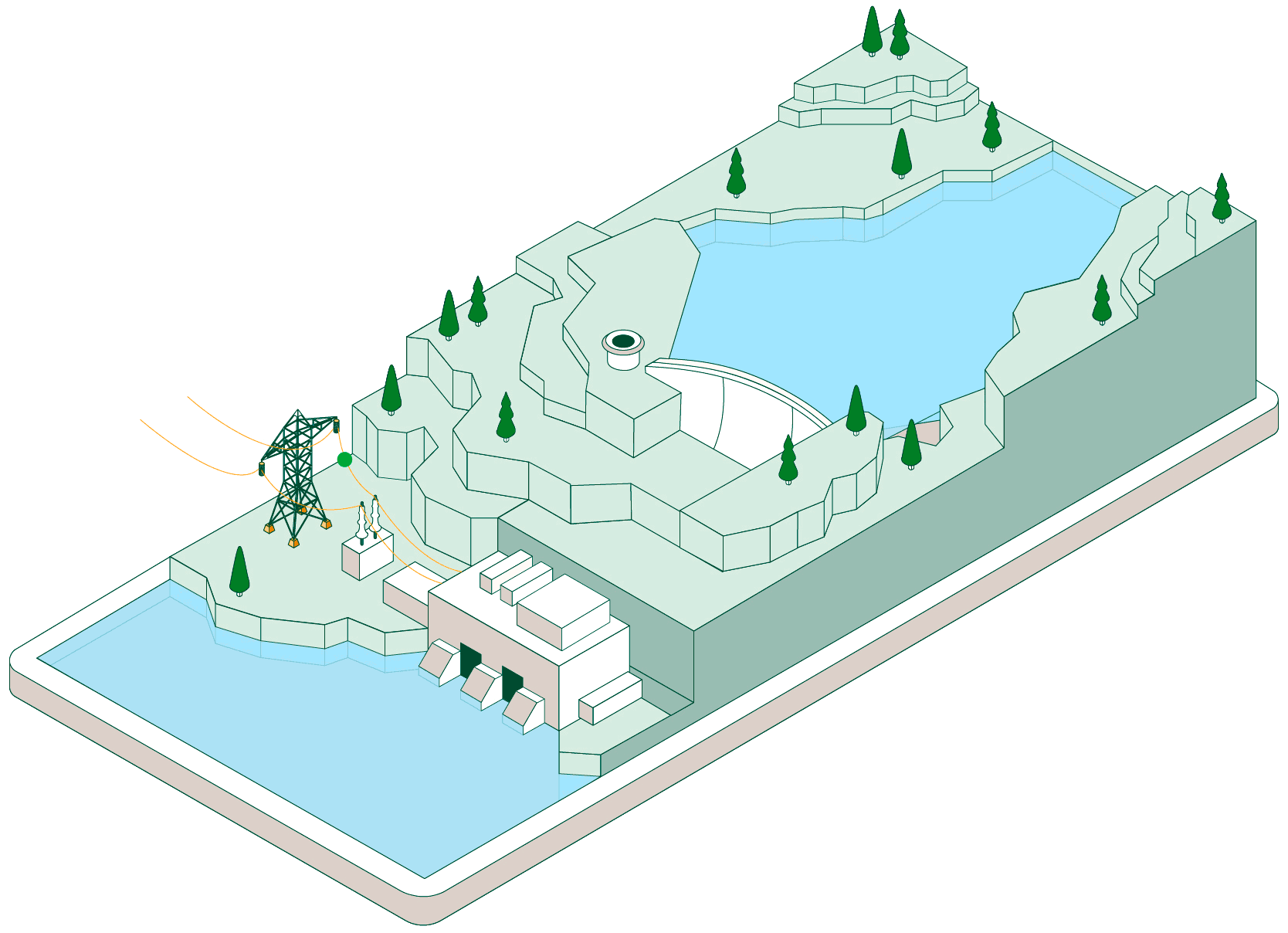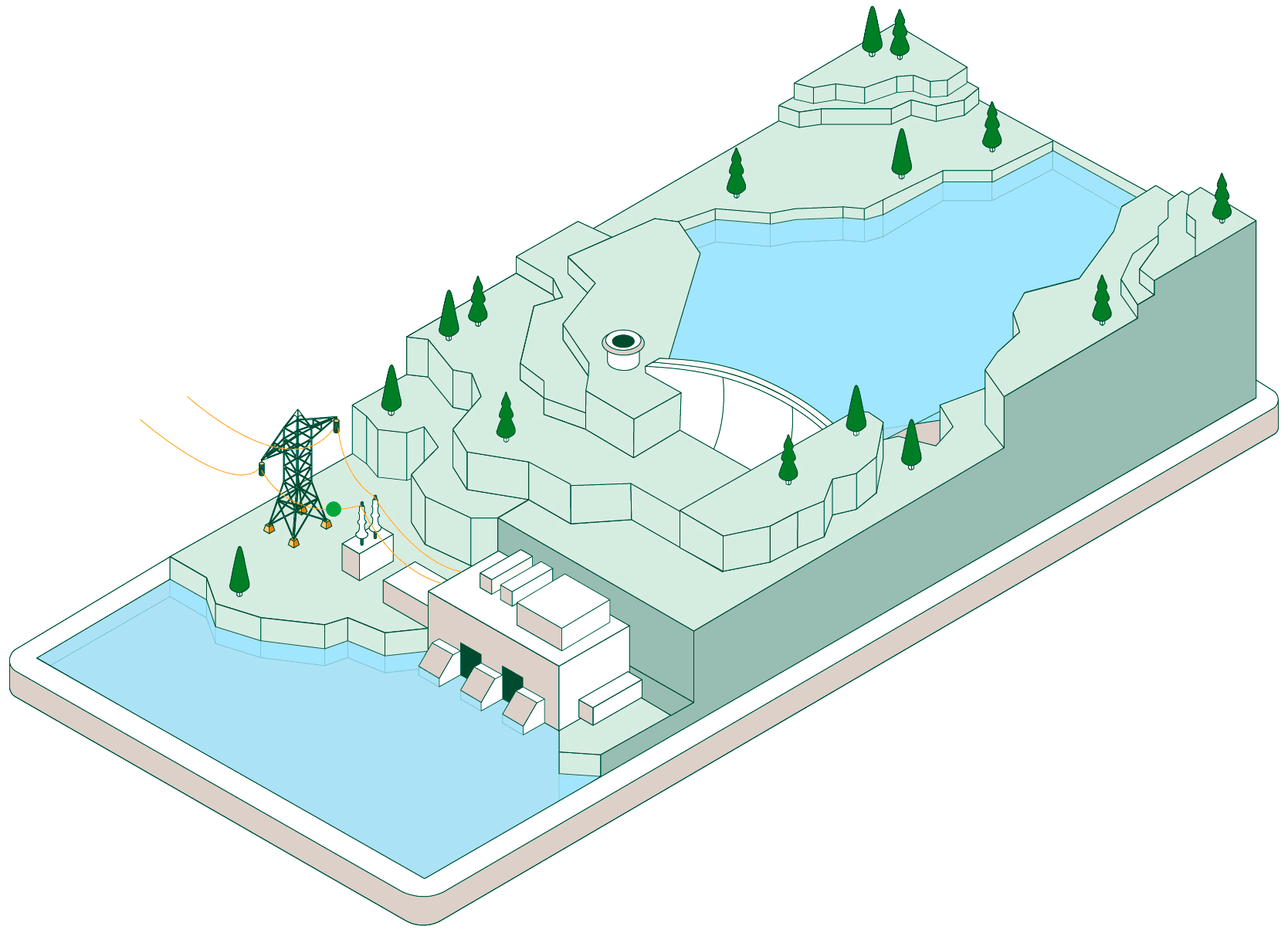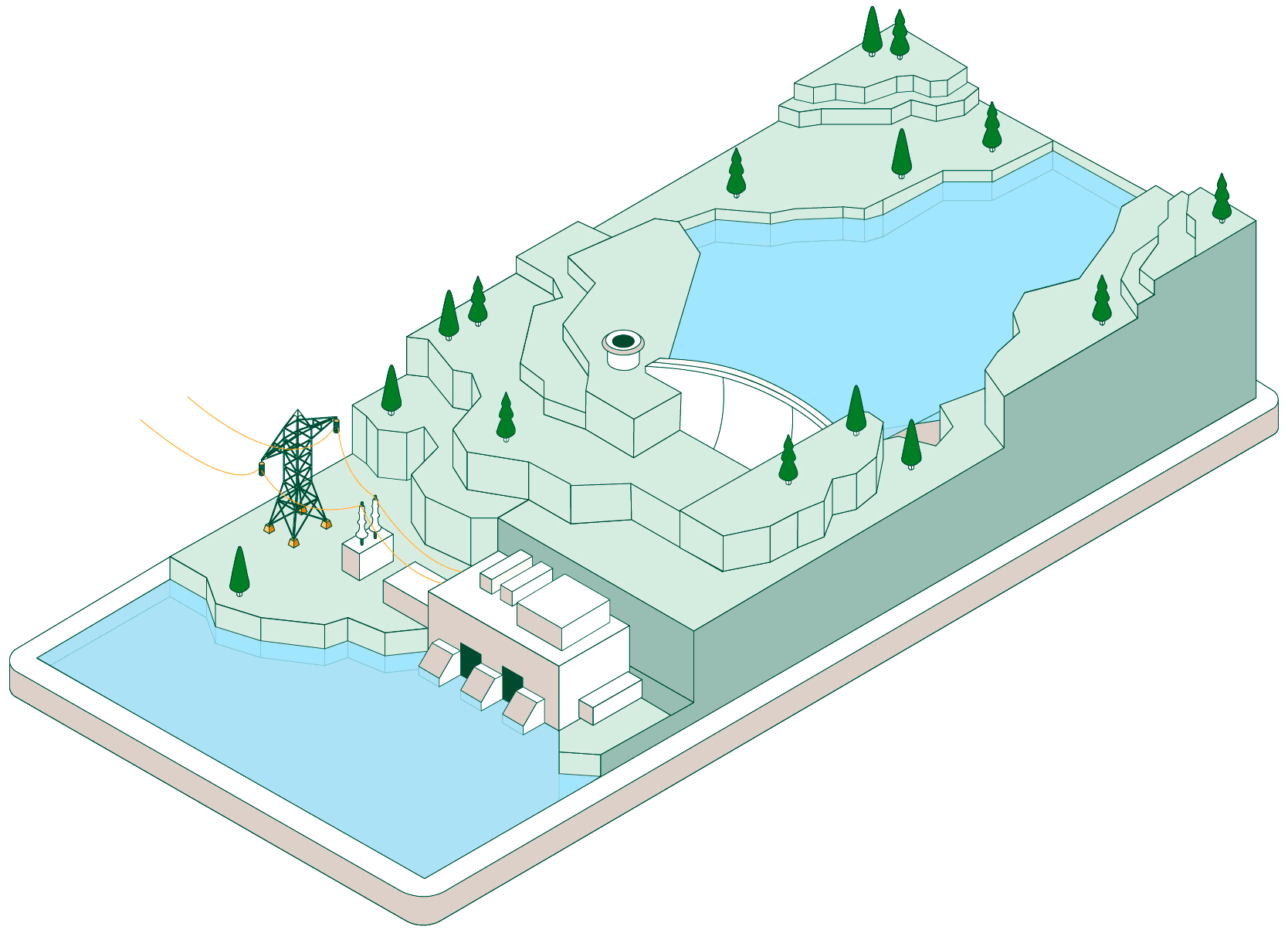
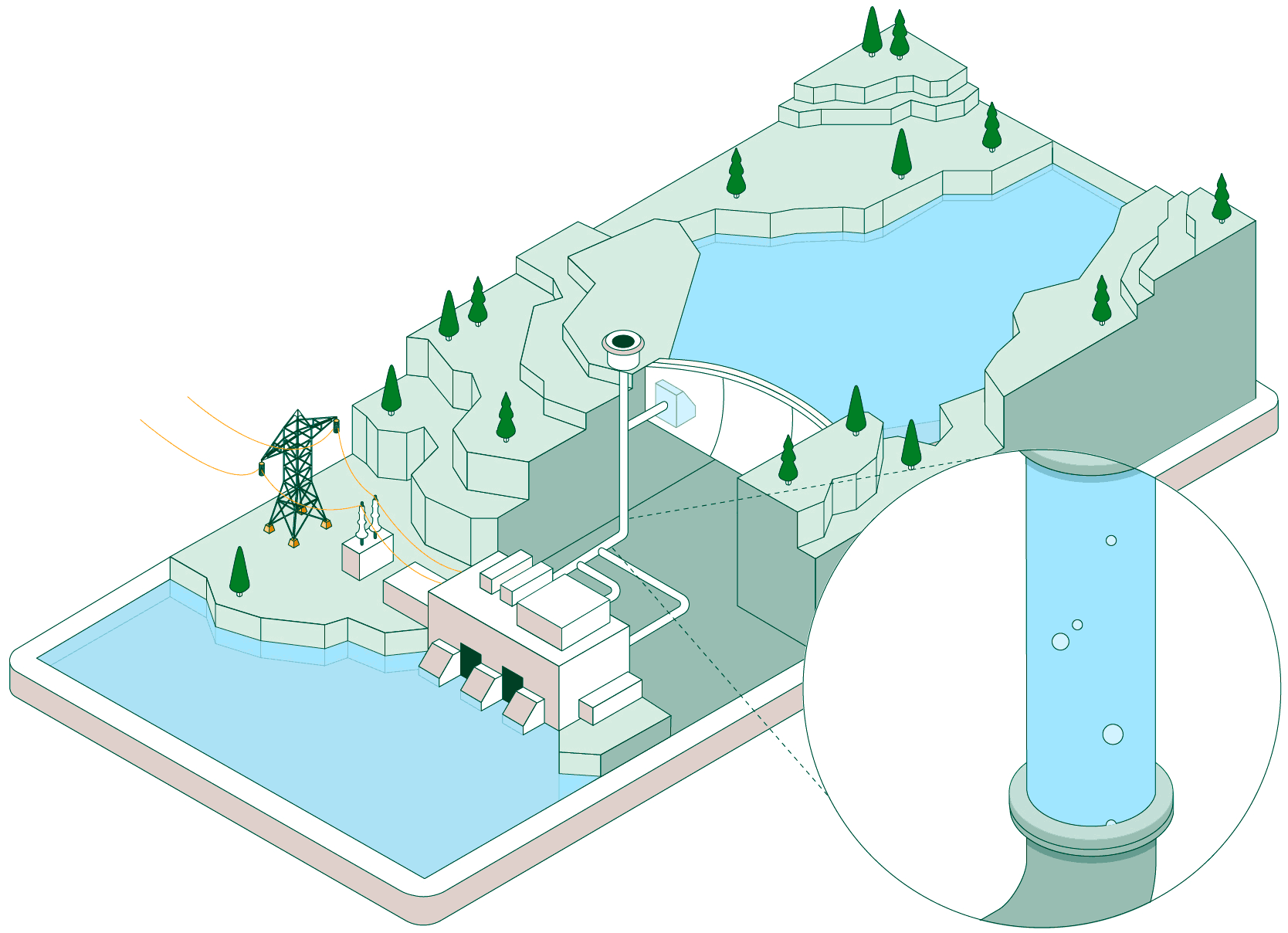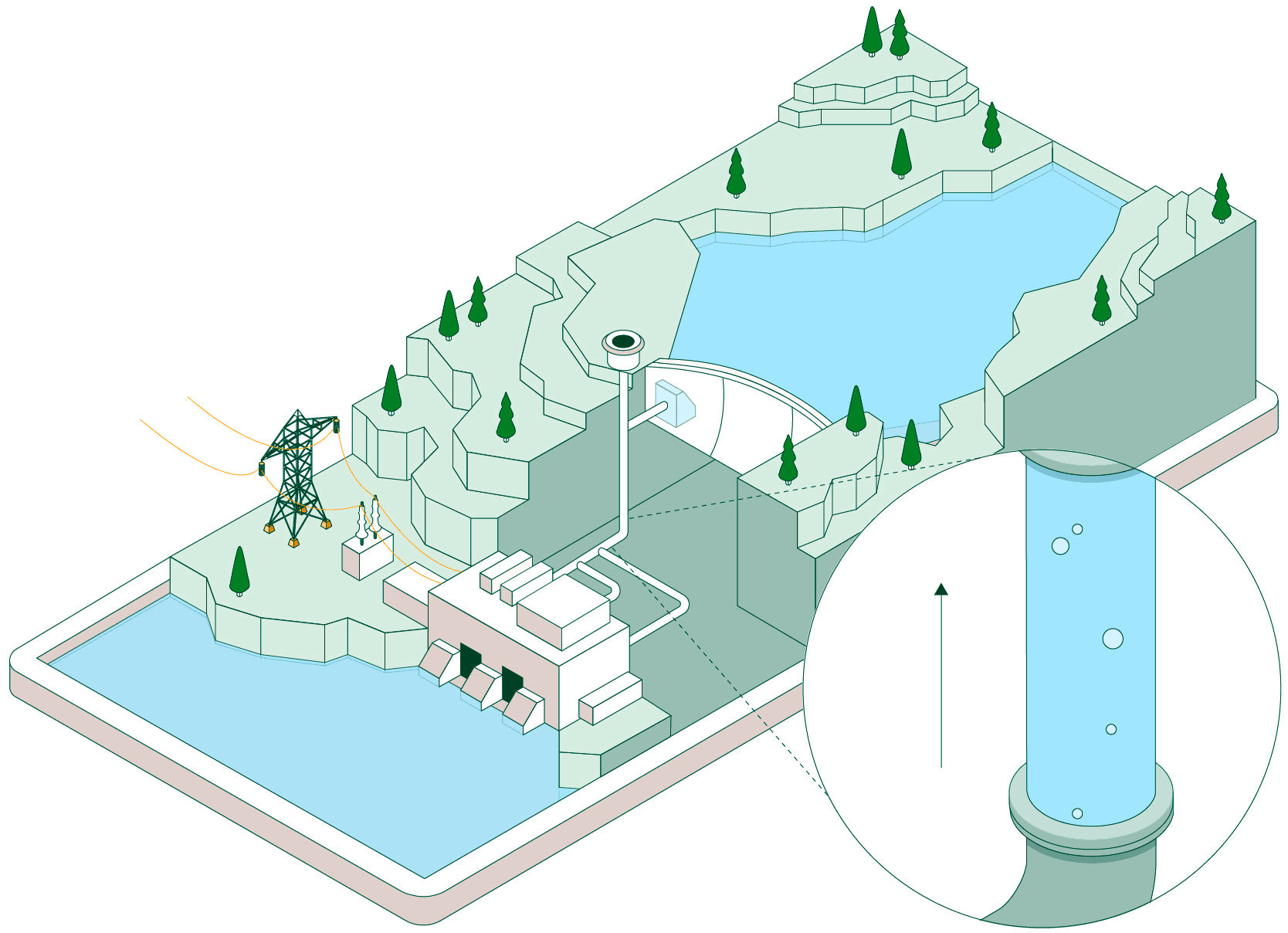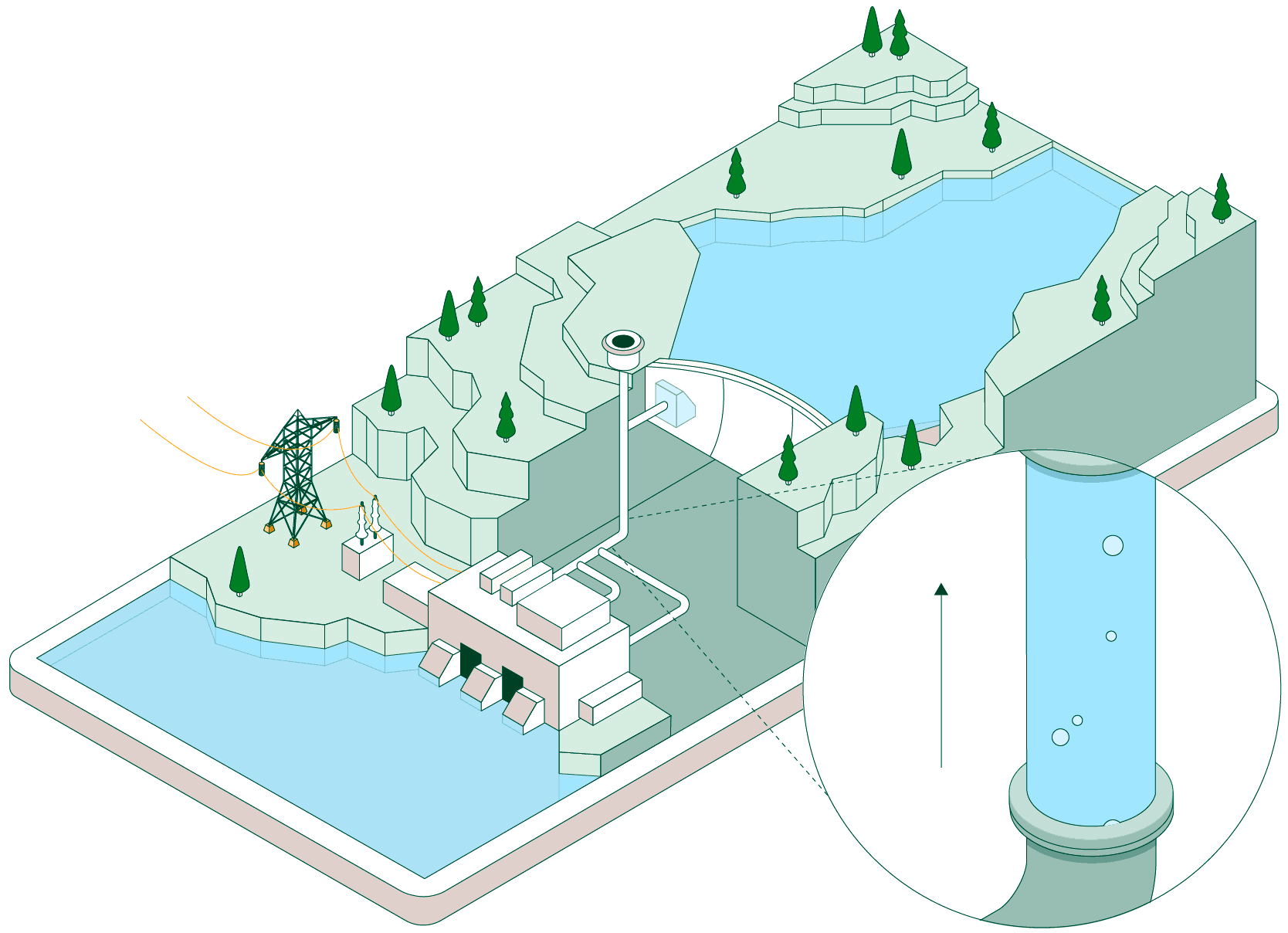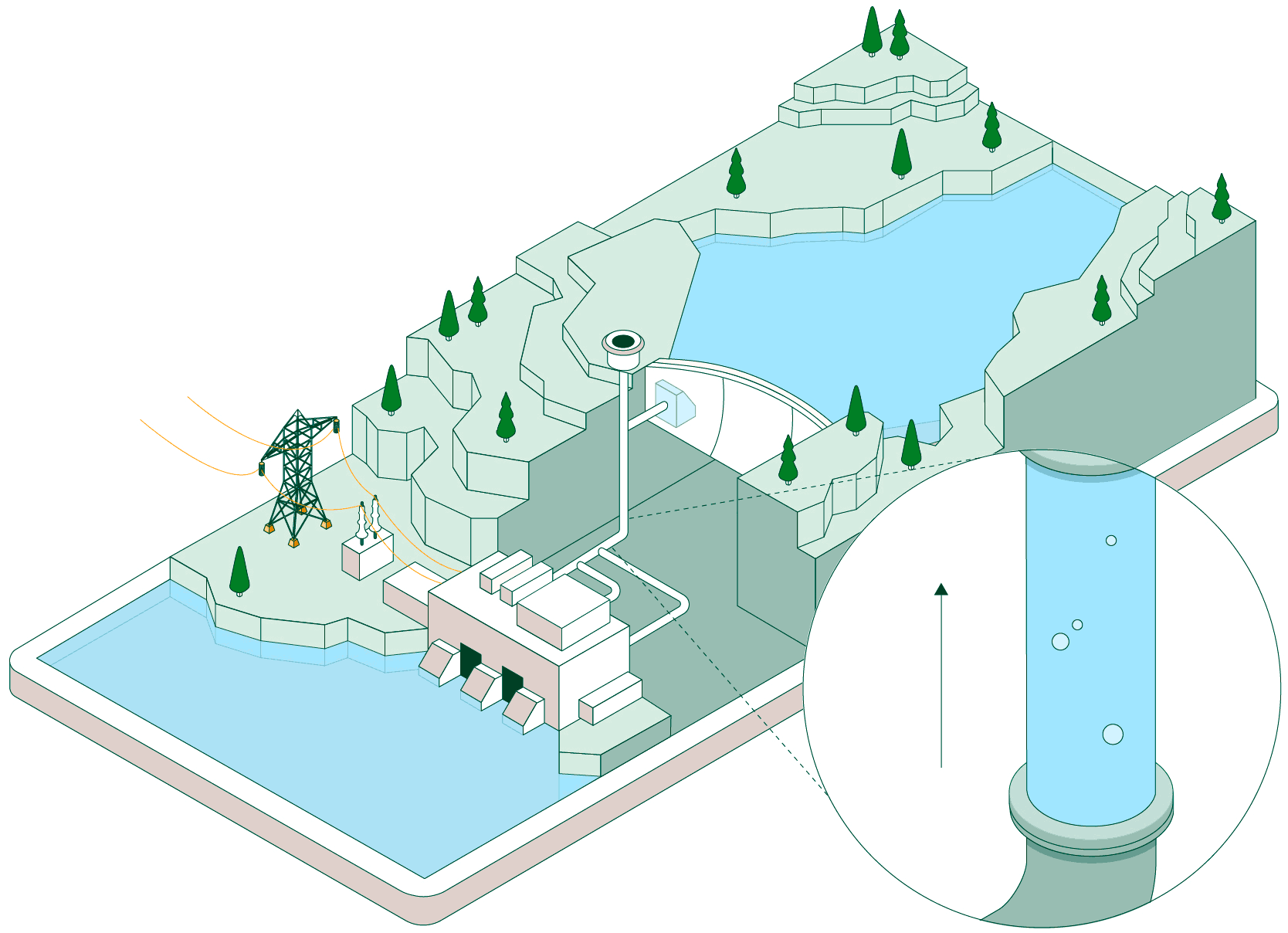
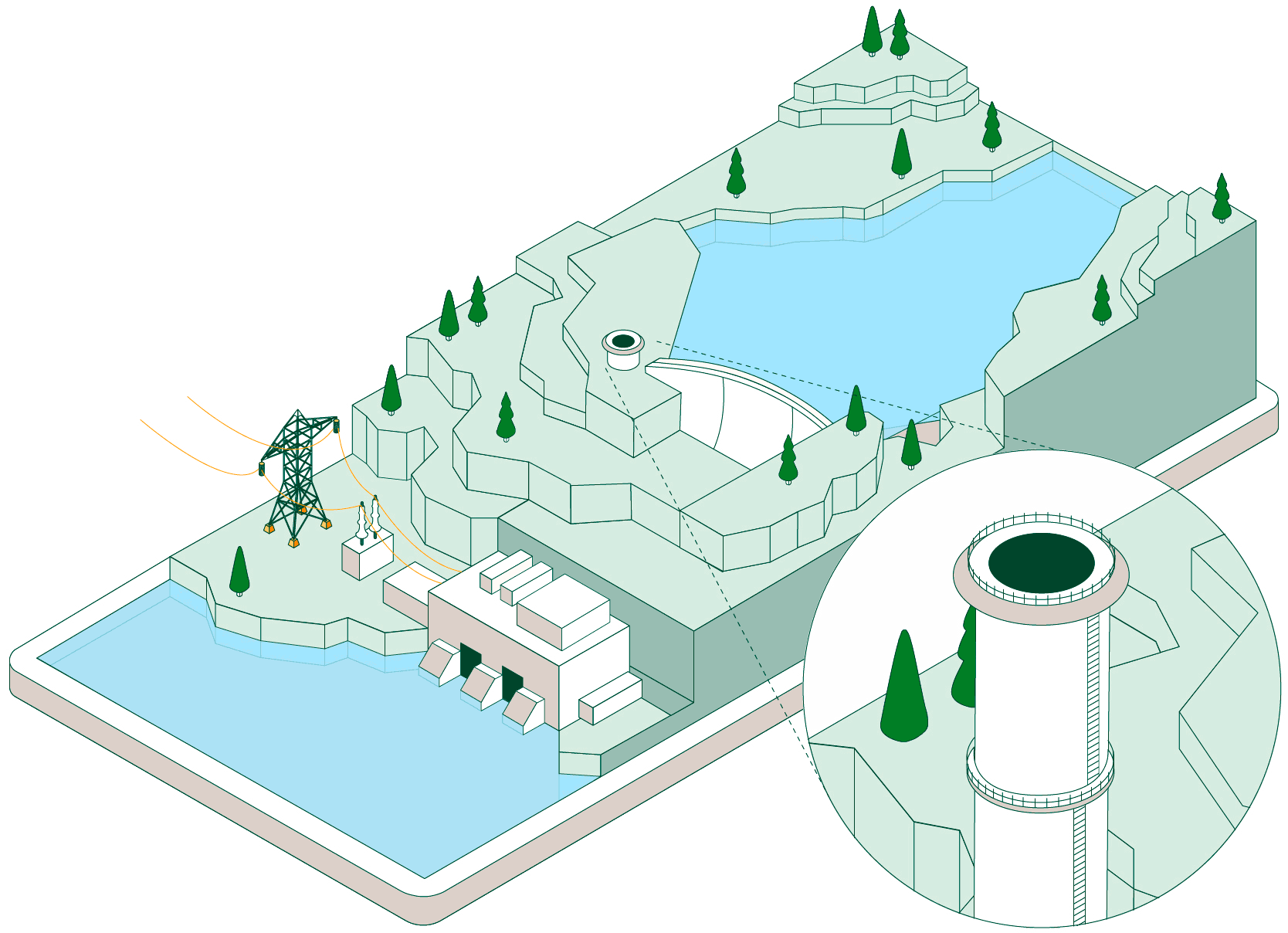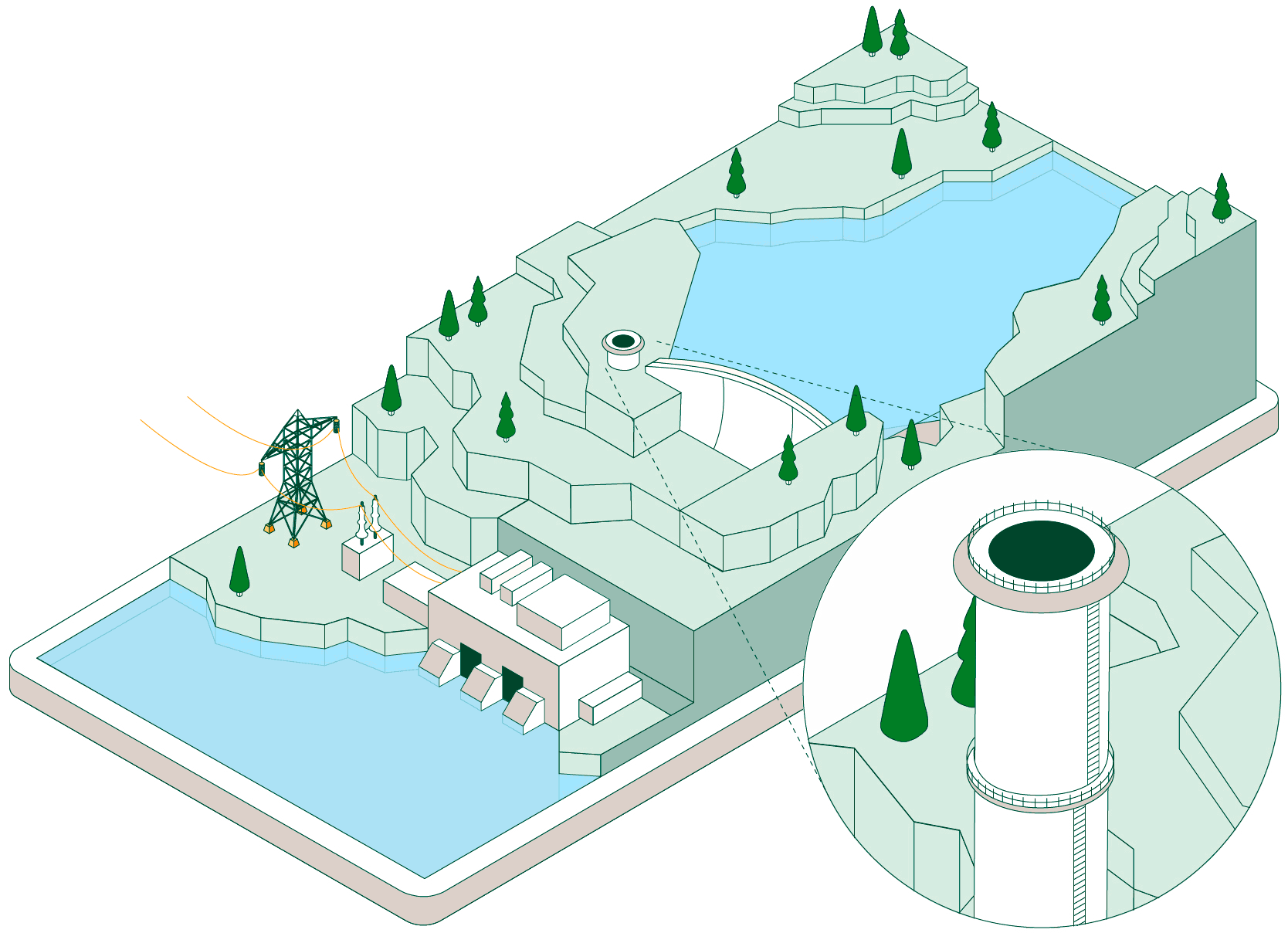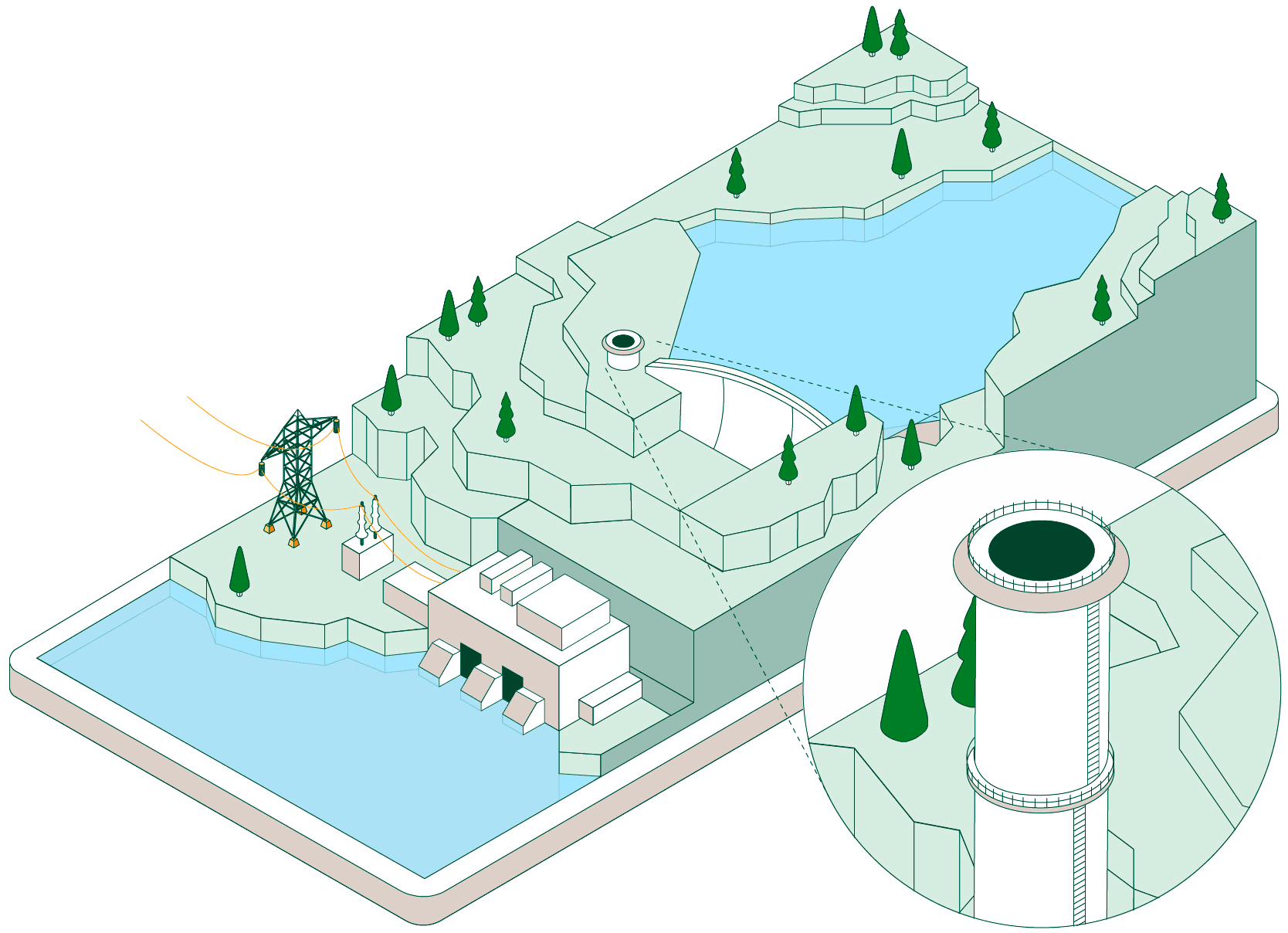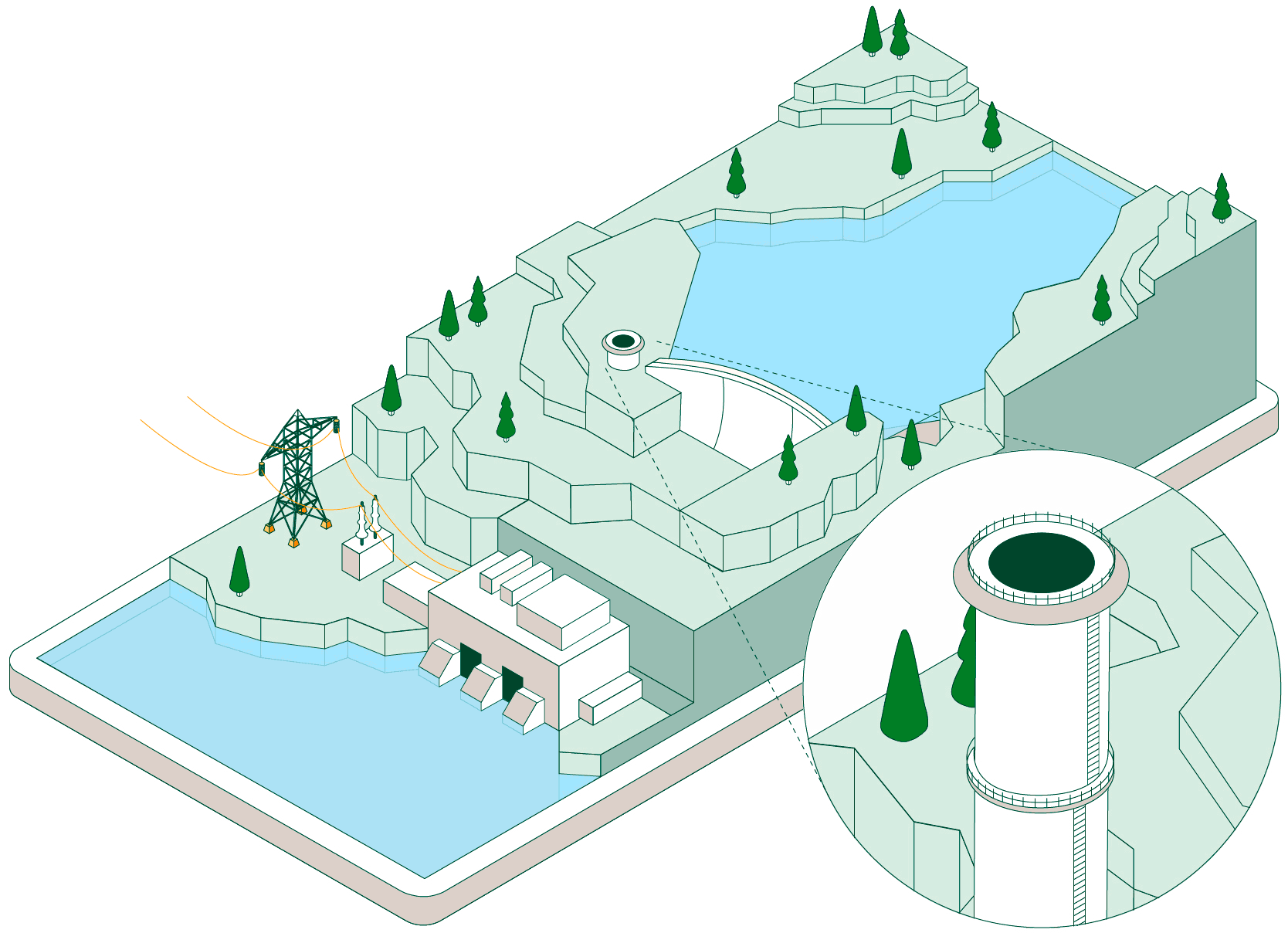
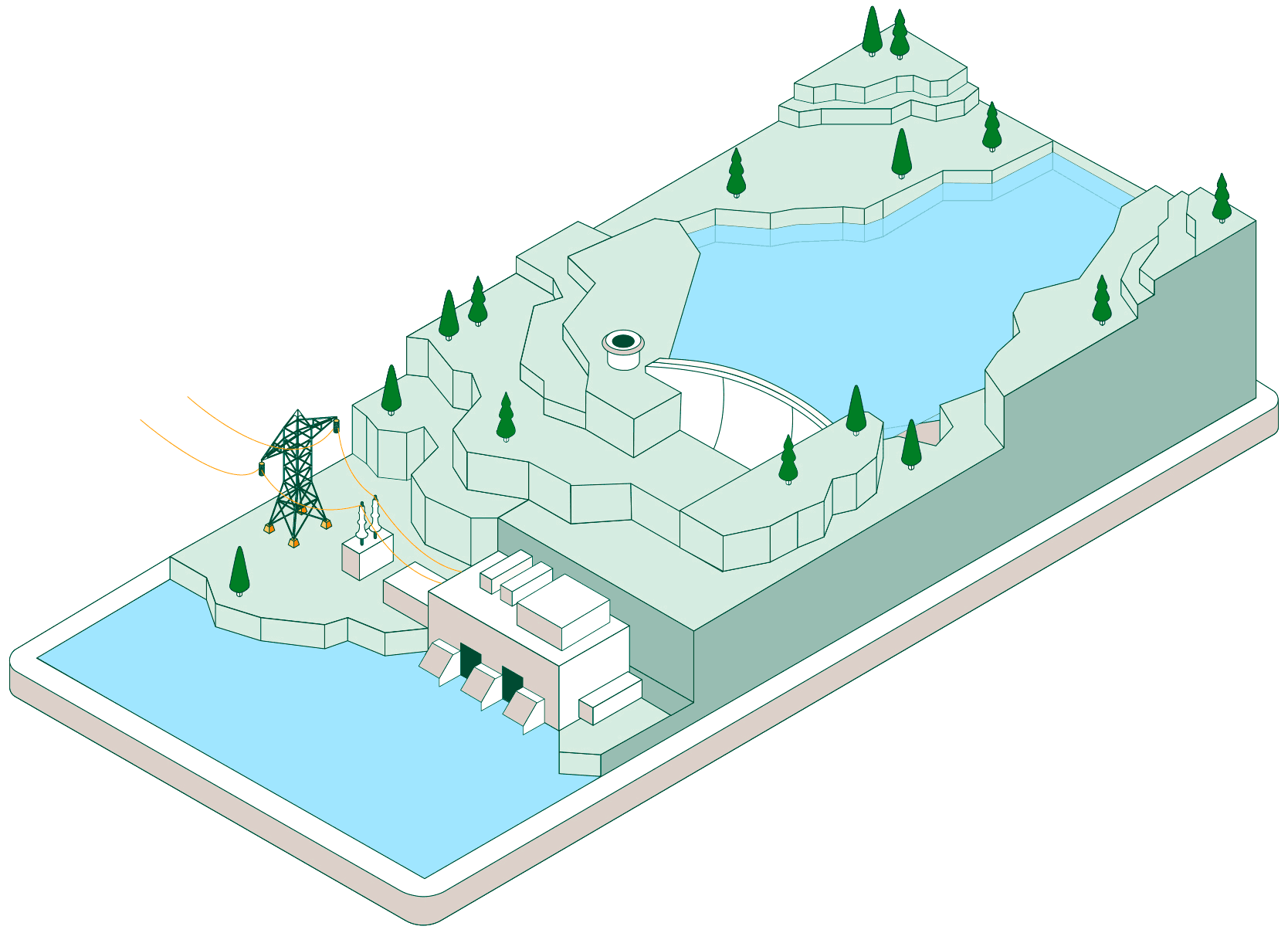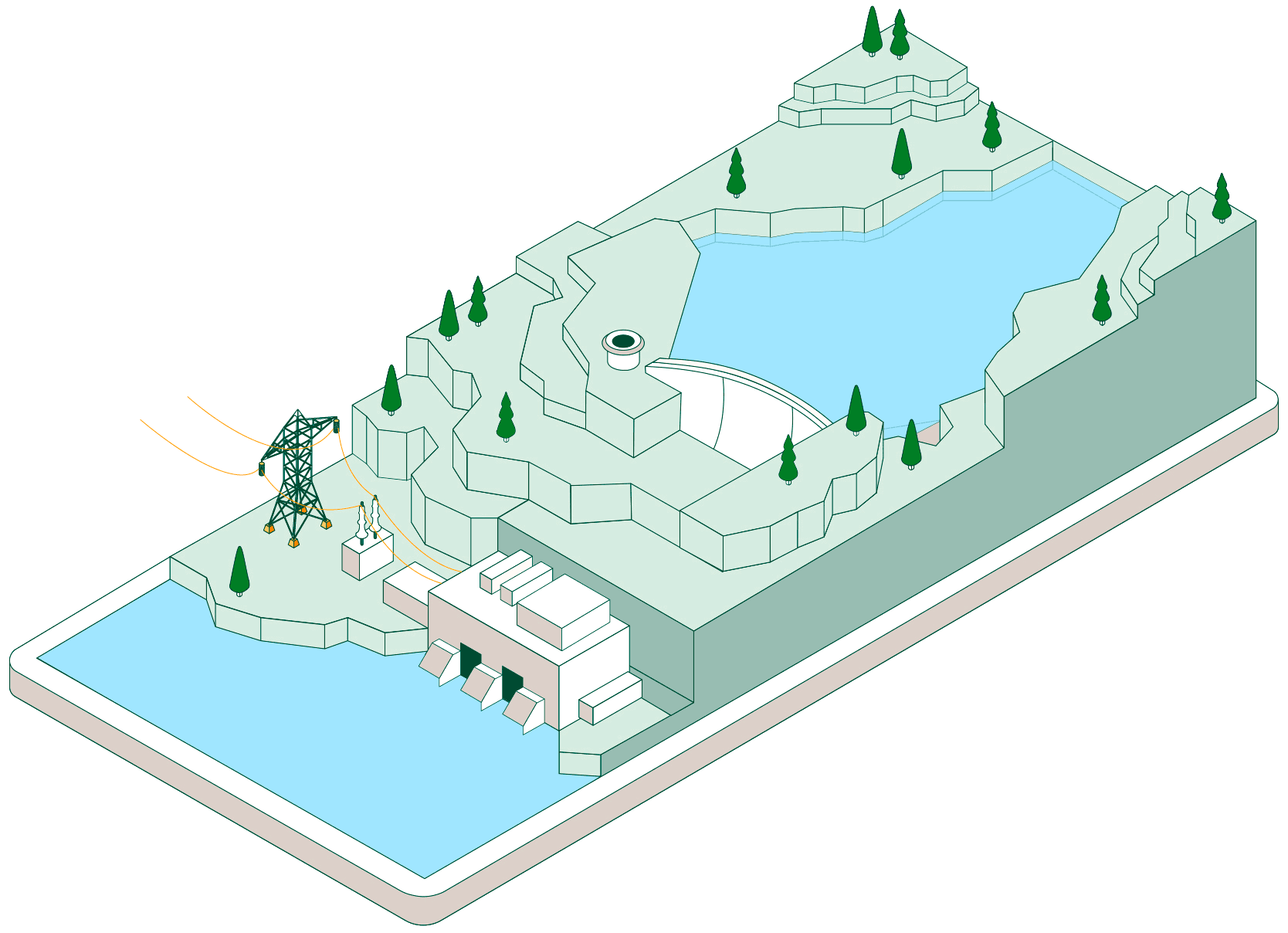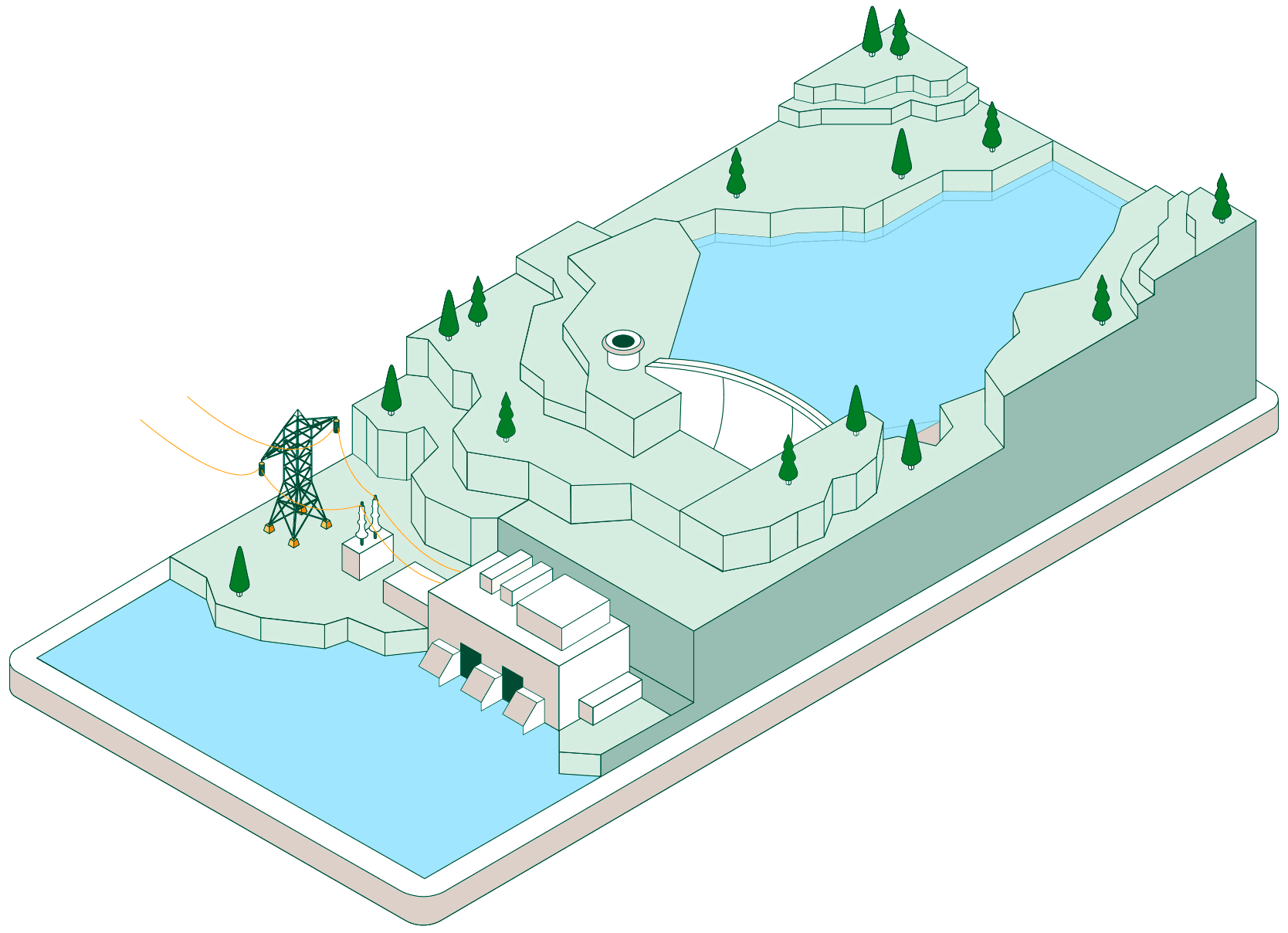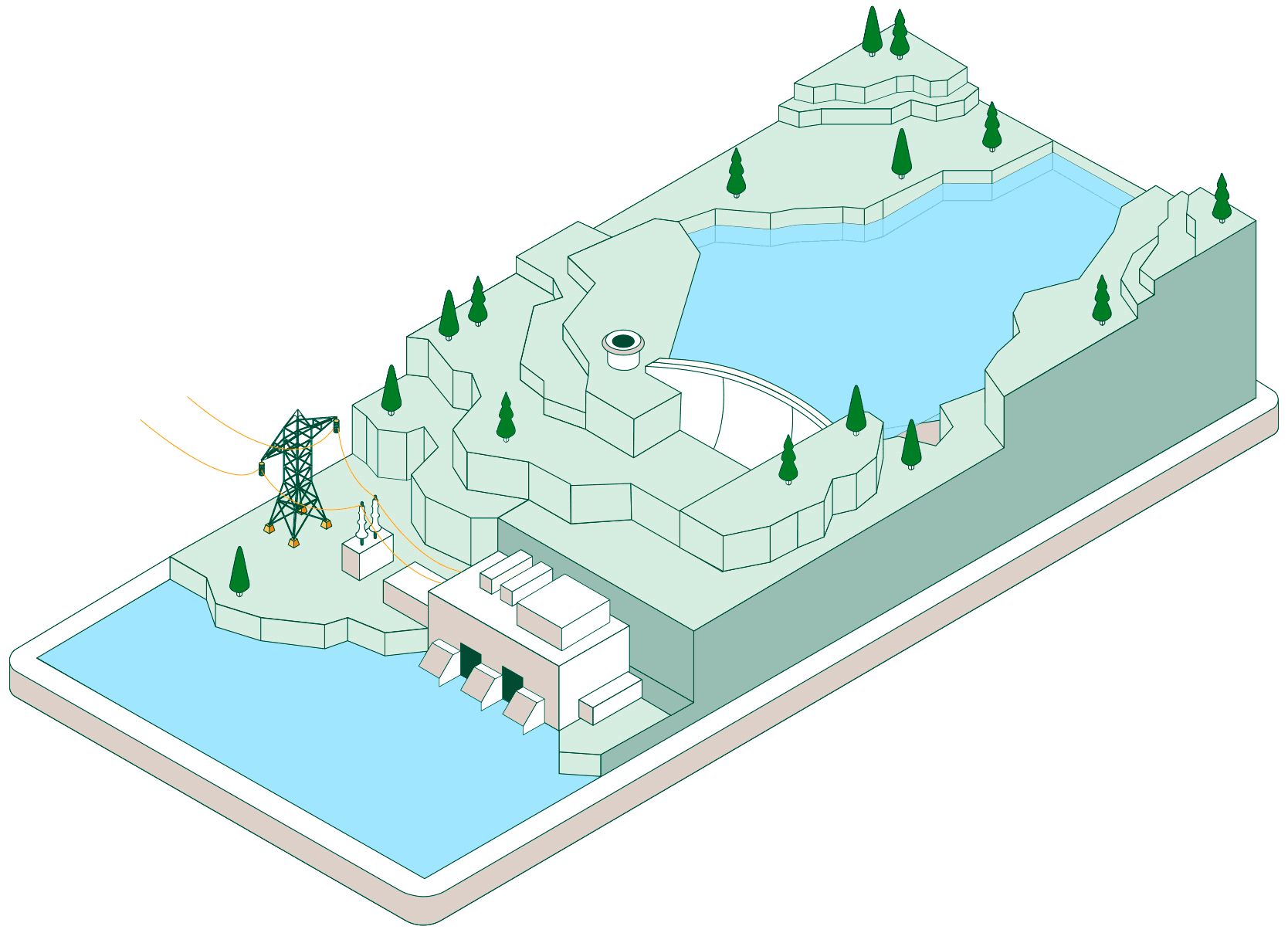
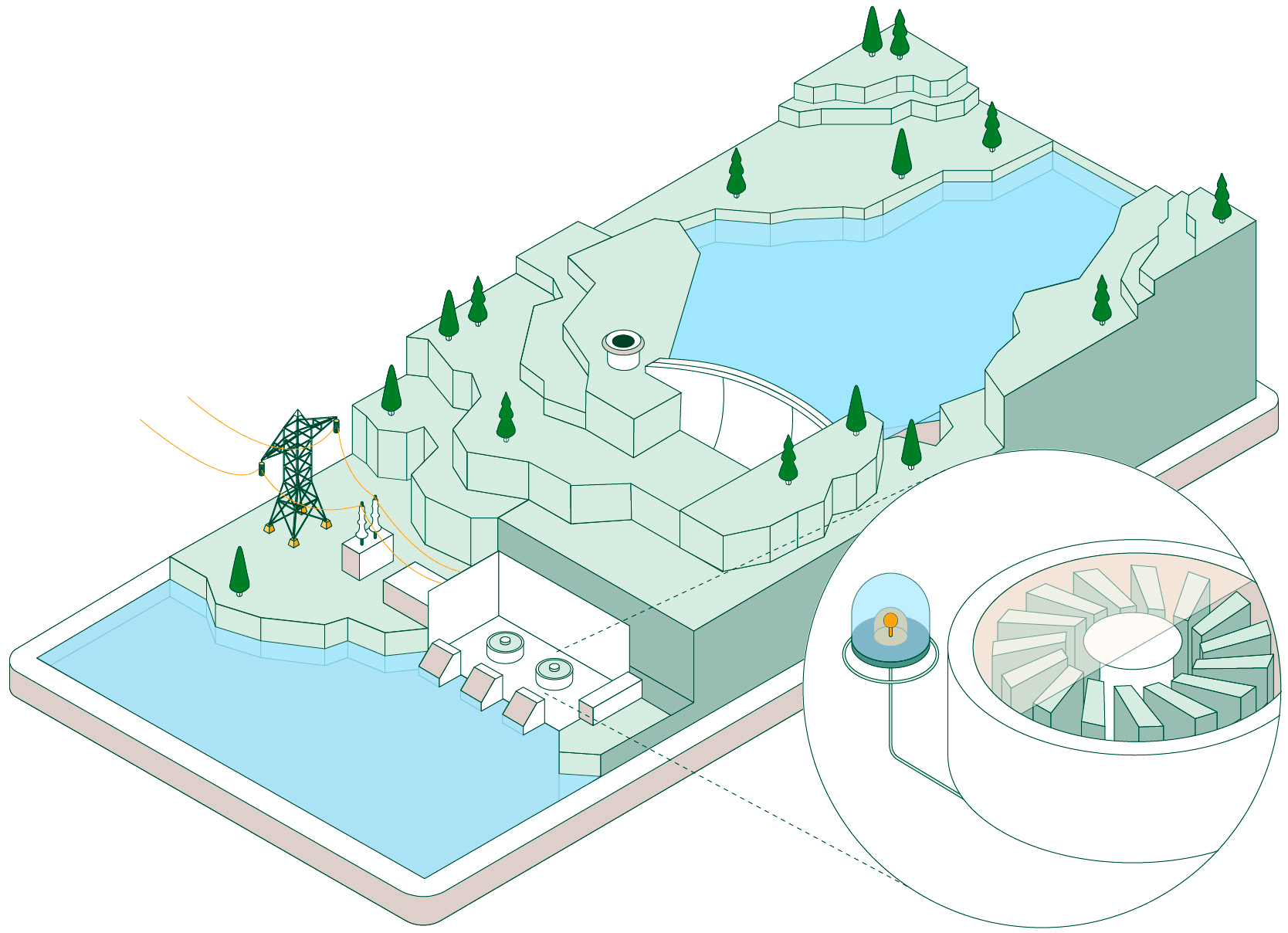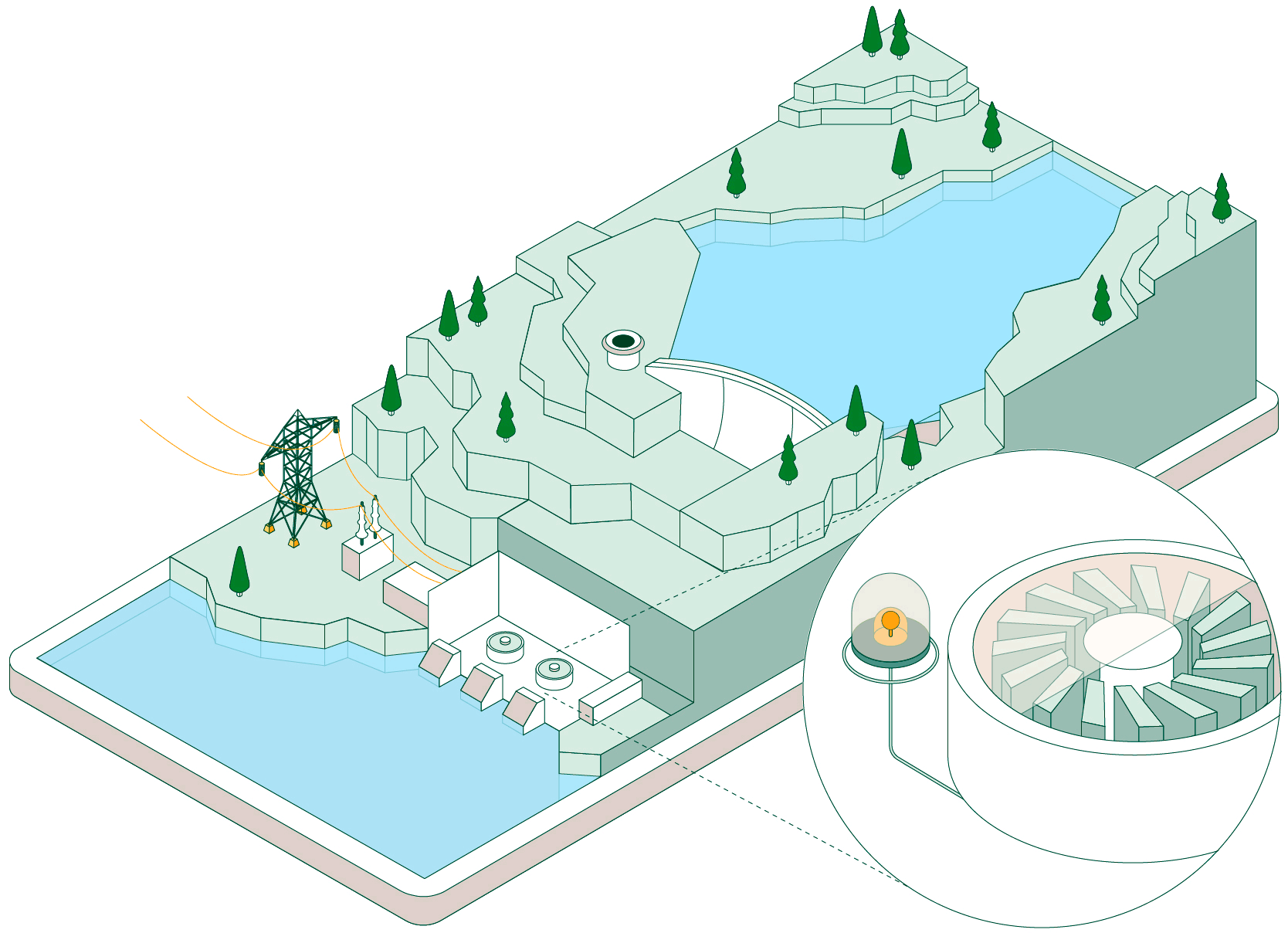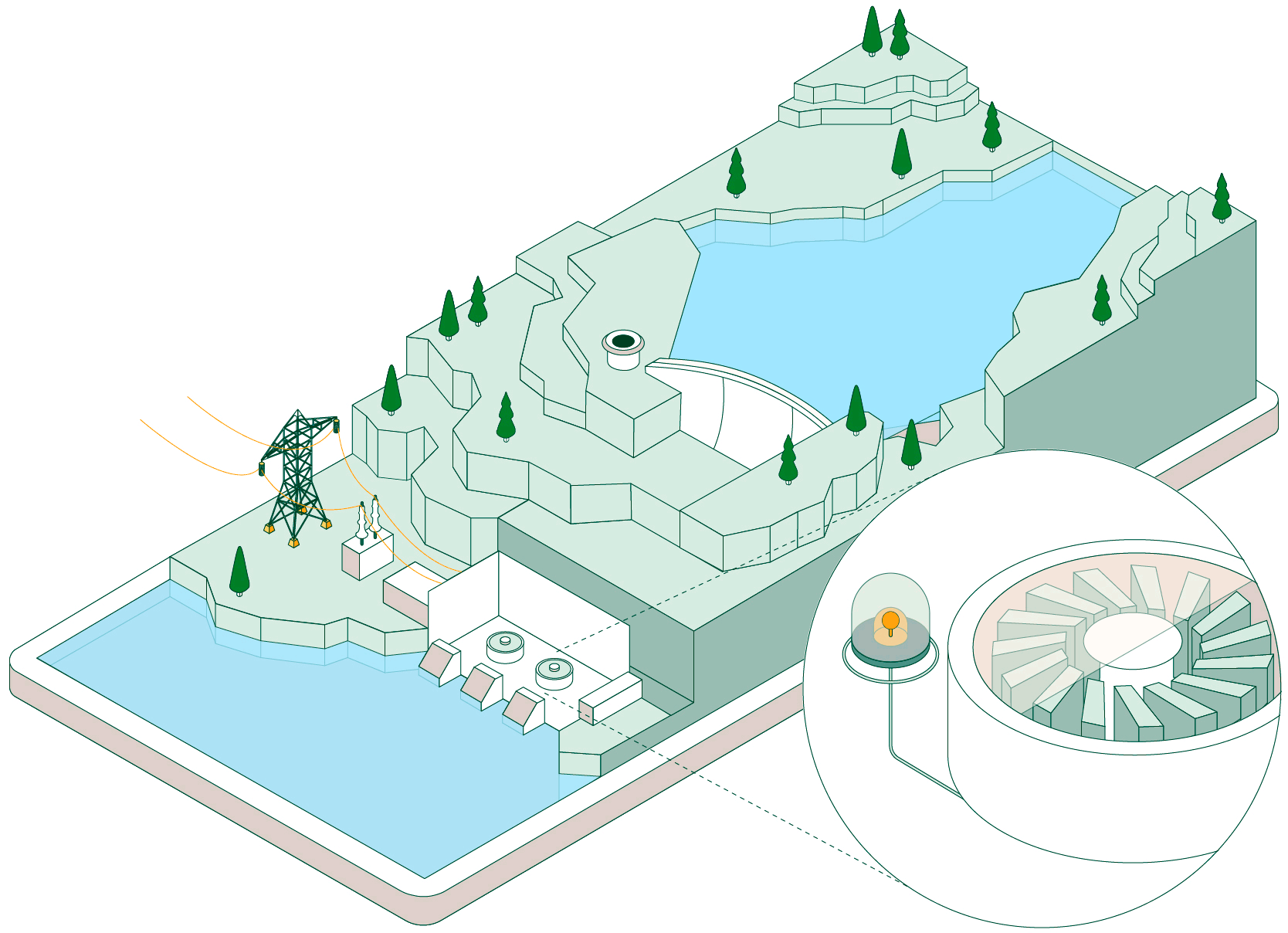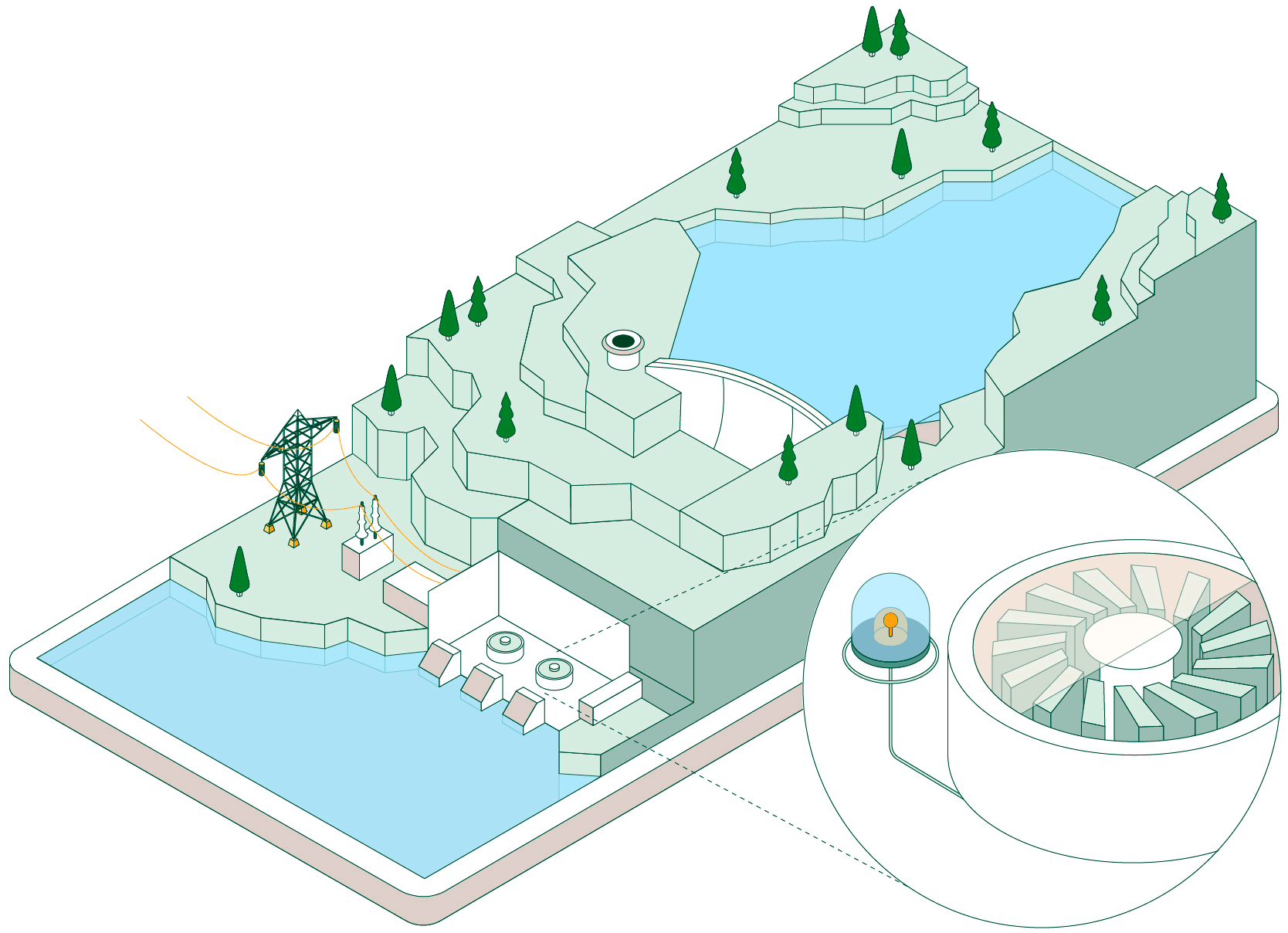
When non-dispatchable renewable generation (photovoltaic or wind, which must be consumed when generated) exceeds electrical demand, the pumped-storage plant begins operating to make use of that surplus energy.
Hydraulic pumps drive water from the lower reservoir up to the upper reservoir through a pressurised pipe and a conveyance tunnel.
To control water pressure during pumping and avoid overpressure, some plants feature a surge shaft or pressure-relief valve systems.
The pumped water accumulates in the upper reservoir, which acts as a large store of potential energy ready to be used when electricity generation is required.
Once the water is stored, the plant can remain idle until the power system needs more energy. At that point, the flow is reversed and the facility operates like a conventional hydroelectric power plant.
Why are pumped-storage hydroelectric plants so important?
Autonomous region: Valencia Region
Province: Valencia
Municipality: Cortes de Pallás
The largest pumped-storage hydroelectric plant in Europe is La Muela II, located at the Cortes de Pallás reservoir on the right bank of the River Júcar.
Its installed capacity reaches 853.6 megawatts (MW) of nominal power in generation and 767.8 MW in pumping – enough to supply the electricity consumption of almost 200,000 households – thus doubling the generation capacity of the Cortes-La Muela complex to nearly 1,500 MW, which would be equivalent to the annual demand of almost 400,000 families.
The plant has four reversible turbine units housed within a cavern that exploit the more than 500-metre difference in elevation between the artificial La Muela reservoir and the Cortes de Pallás reservoir to produce electricity.
Installed pumping capacity: 767.8 MW

Embalse de Cortes de Pallás
Autonomous region: Castilla and León
Province: Salamanca
Municipality: Villarino de los Aires
The Villarino plant plays a vital role with its 810 MW of nominal generation power and 726 MW of pumping capacity. This facility produces clean, renewable hydroelectric energy to supply nearly half-a-million households. It takes advantage of the nearly 400-meter difference in elevation between the Almendra reservoir – Spain’s third-largest – and the power station, which are both located in Salamanca province.
Installed pumping capacity: 726 MW

Presa de Almendra
Autonomous region: Ourense
Province: Galicia
Municipality: Vilariño de Conso
Located on the left bank of Las Portas reservoir, in the municipality of Vilariño de Conso in Ourense, the Conso plant has a nominal generation power of 228 MW and 207 MW in pumping. The plant operates by either pumping or turbining water between two reservoirs – the upper Las Portas and the lower Bao – separated by a 230-meter difference in elevation.
Installed pumping capacity: 207 MW

Embalse de Las Portas
Country: Portugal
Location: Río Tâmega (northern Portugal)
Another of the group’s major pumped-storage initiatives is the Tâmega hydroelectric complex, made up of three new power plants along the river of the same name, which is a tributary of the Douro located in northern Portugal, near Porto. Gouvães and Daivões began operating in early 2022, while Alto Tâmega has been operational since 2024.
Together, the three plants have an installed capacity of 1,158 MW, increasing the country’s total installed electric power by 6%. The Gouvães plant is the one equipped with pumping capacity, with 880 MW of power. The complex can generate 1,766 GWh per year, enough to meet the energy needs of nearby municipalities and the cities of Braga and Guimarães – roughly equivalent to the demand of 440,000 homes.
Installed pumping capacity: 207 MW

Embalse de Las Portas
Autonomous region: Castilla and León
Province: Salamanca
Municipality: Aldeadávila de la Ribera
The Aldea II plant is located in the municipality of Aldeadávila de la Ribera, in the province of Zamora, and has a nominal generation capacity of 421 MW and 400 MW in pumping. It houses two reversible turbine units in a cavern that pump water from the Saucelle reservoir to the Aldeadávila reservoir, with a height difference of more than 110 meters between them.
Installed pumping capacity: 400 MW

Embalse de Aldeadávila
Efficient energy storage is a cornerstone of the strategic process to stabilize market prices and avoid margin volatility. At Iberdrola, we are leaders in pumped-storage technology, and through our new Strategic Plan 2025-2028, we aim to strengthen this position with an investment of €1.5 billion in the storage area.
By 2026, we plan to reach 120 million kWh of pumped-storage capacity – a 20% increase – with a total portfolio of 150 million kWh. This firm commitment will enhance the stability of the electricity system, alongside growth in smart grids, manageable renewables and hybridization.
06 February 2025
More about hydroelectric power