International Day for Biological Diversity: global commitment to nature
What is biodiversity and why is it important?
International Day for Biological Diversity, which is celebrated on 22 May, is a global initiative by the United Nations to raise awareness about the importance of protecting biodiversity and promoting sustainable coexistence among all forms of life on the planet. At the Iberdrola Group, we integrate the conservation and promotion of biological diversity into our strategy and work to contribute to preserving natural ecosystems, guaranteeing a more environmentally friendly future.
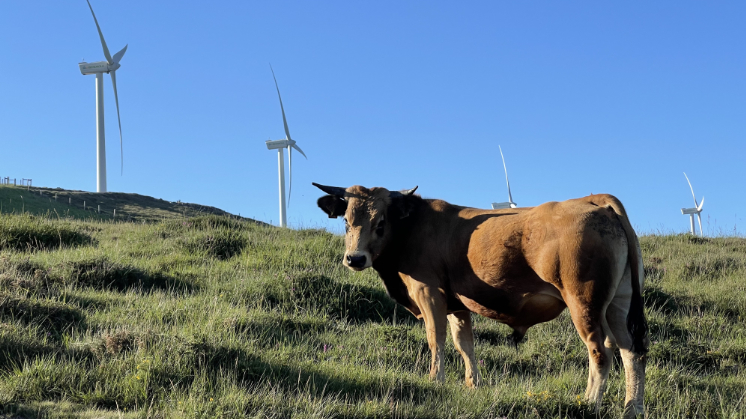

Iberdrola in respect for and preservation of biodiversity
At Iberdrola, we work to promote protection and action for nature and the planet's life forms. We have set ourselves the ambitious goal of having a net positive impact on biodiversity by 2030. This commitment has been strengthened through our Biodiversity Plan 2030, which establishes the mechanisms to achieve this goal and drive the transformation towards an energy model in harmony with nature and human beings.
This roadmap addresses the impact on ecosystems and species of the Group's business throughout its life cycle, considering the supply chain and creating economic and social value through ecosystem services. The plan is based on applying the conservation hierarchy principle and implementing mechanisms to identify, quantify and monitor compliance.
The basis for this Plan was the approval in 2007 of our Biodiversity Policy, which is integrated into Iberdrola's Governance and Sustainability System. The Plan is based on years of work in integrating the consideration of biodiversity into strategic planning and corporate decision-making.
Why is it important to conserve biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the essential building block of life on Earth. Every species, from large mammals to the smallest micro-organisms, has a specific role to play in maintaining the balance and resilience of life on the planet. On all of them, in their wide variety, depends the existence of other forms of life and the regular functioning of ecosystems, providing essential natural services and benefits such as food production, climate regulation, water and air purification and the possibility for different living beings to have a home.
Biodiversity is also an invaluable source of innovation and well-being. Many of the medicines, materials and technologies we use today have their origins in nature. The enormous genetic variety of the diversity of living things offers opportunities to adapt to future changes, such as the development of crops that are more resistant to extreme weather or new treatments for diseases. We could say then that preserving biodiversity is an investment in our own future and in the ability to find solutions to challenges we may face.
Its value can also be conceived from an ethical perspective. Biodiversity represents a natural heritage that we must pass on to future generations. Every species that goes extinct and every ecosystem that is destroyed are irreparable losses that impoverish the richness of life on the planet. Respecting all forms of life on earth and their diversity is therefore an act of responsibility that reminds us that human beings are part of a much wider web of life.
The reasons are diverse, but the conclusion is the same: conserving biodiversity means preserving the processes that make our survival and that of millions of life forms possible. Without it, our planet would not be a place we could live.
What is the impact of biodiversity loss on the planet?
Biodiversity loss has profound and often irreversible consequences for the health of planet Earth. The disappearance of species and the degradation of natural habitats weakens the ability of ecosystems to stay in good health and sustain other forms of life or to adapt to environmental change. This increases our vulnerability to crises such as food insecurity, emerging diseases, the spread of pests or natural disasters.
The deterioration of biodiversity also accelerates climate change and exacerbates its effects, creating a feedback loop that threatens both nature and society. A clear example is forests and oceans, whose ample capacity to absorb CO2 decreases if their ecosystems are weakened and their biodiversity is reduced or even extinguished.
Biodiversity loss therefore poses a cascading threat to the survival of different forms of life on Earth. For humans, the consequences are obvious: the extinction or minimisation of biological diversity endangers our food supply, our health and our well-being.

Trees Programme
We promote planting as part of our Trees programme.

Biodiversity protection
We protect and preserve biodiversity on some of our projects.

Biodiversity loss
A risk for the environment and for humanity.
What is the commitment of the International Day for Biological Diversity?
The International Day for Biological Diversity encourages governments, businesses, communities and people to act decisively to protect and restore biological diversity every 22 May. Under annual slogans that ask us to take action, the day promotes the implementation of sustainable policies, strengthened protection of protected areas, the restoration of degraded habitats and public awareness.
Origins of the International Day for Biological Diversity
The International Day for Biological Diversity was proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity. It was originally celebrated on 29 December to commemorate the date the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) Enlace externo, se abre en ventana nueva. entered into force, an international agreement signed during the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to protect biodiversity, promote the sustainable use of its resources and ensure its benefits were shared fairly.
Enlace externo, se abre en ventana nueva. entered into force, an international agreement signed during the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to protect biodiversity, promote the sustainable use of its resources and ensure its benefits were shared fairly.
However, in 2000, the UN decided to change the date to 22 May to make sure it didn’t coincide with end-of-year celebrations that made it difficult to organise awareness-raising events and to ensure greater global participation. Since then, every 22 May, governments, organisations and people around the world come together to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
International Day for Biological Diversity 2025 Theme
The central theme of International Day for Biological Diversity 2025 is ‘Harmony with nature and sustainable development’. This approach highlights the link between conserving biodiversity and moving towards development that meets today's needs without compromising the resources and health of the planet for future generations. This year's celebration aims to instil a sense of urgency and to encourage greater awareness and rolling out actions that integrate sustainable practices in all sectors of society, promoting a balanced and respectful coexistence with the natural environment.
The specific objectives of International Day for Biological Diversity 2025, according to the CBD secretariat, are:

A flock of sheep at the Núñez de Balboa photovoltaic plant (Extremadura, Spain).

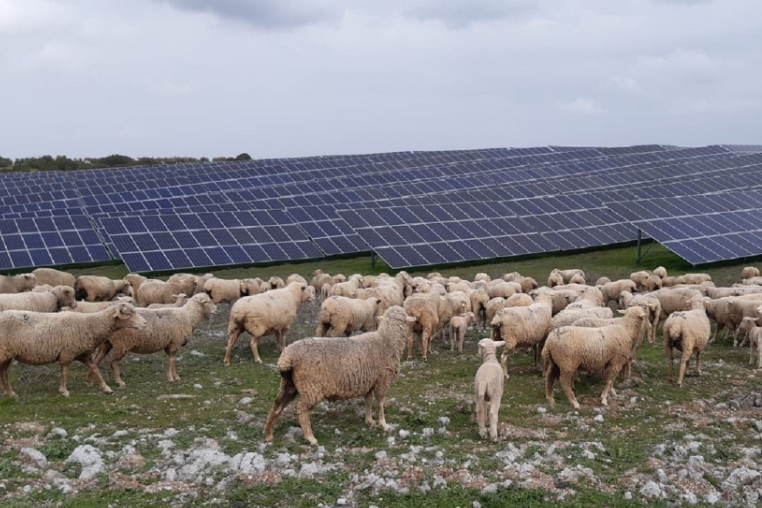
A horse at the Elgea-Urkilla wind farm (Basque Country, Spain).
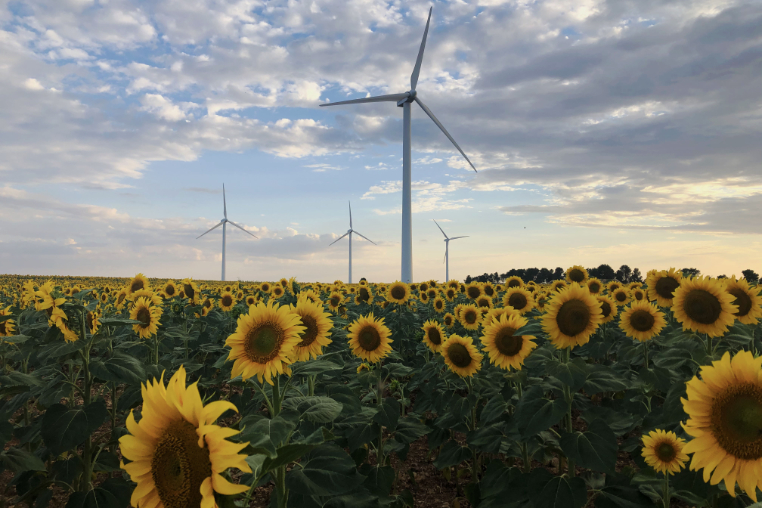

Flora at the Carrasquillo wind farm (Castilla y León, Spain).
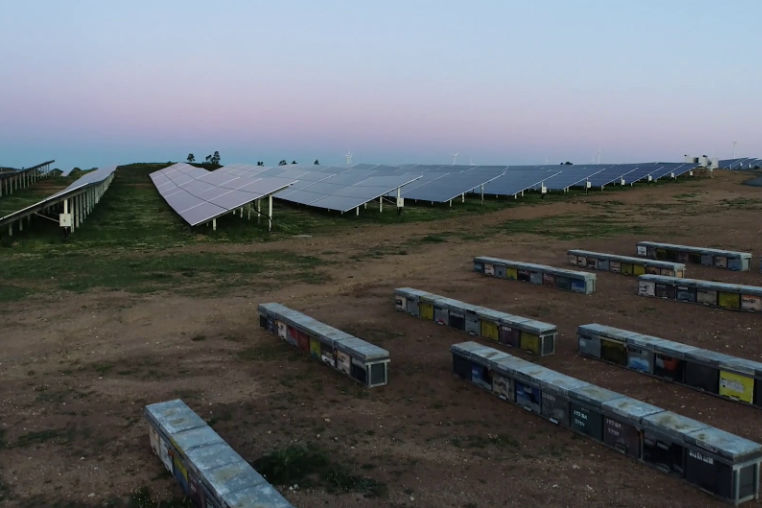

Beehives at the Andévalo photovoltaic plant (Andalusia, Spain).
The Future of Biodiversity: Challenges and Solutions
Biodiversity faces unprecedented threats. While natural phenomena influence its status and evolution, human action puts increasing pressure on the planet's species and ecosystems. Habitat loss through urban and agricultural expansion, pollution, climate change, the introduction of invasive species and overexploitation of natural resources (including rampant deforestation) are driving extinction to an alarming level. As a result, nearly 40 per cent of the planet's terrestrial species could disappear by 2050, according to a study published in the journal Nature External link, opens in new window. .Enlace externo, se abre en ventana nuev
External link, opens in new window. .Enlace externo, se abre en ventana nuev
In the face of these challenges, there are obvious and urgent solutions, as the choices we make today will determine how species will coexist in the years to come. Conserving protected areas, restoring degraded ecosystems, protecting key species, moving towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns and promoting a low-carbon economy are key. It is also essential to integrate biodiversity into public policy, boost science and environmental education, research new technologies for conservation, and promote collaboration between governments, businesses and citizens. Only through a joint and coordinated approach will it be possible to halt biodiversity loss.
Iberdrola in respect for and preservation of biodiversity
At Iberdrola, we work to promote protection and action for nature and the planet's life forms. We have set ourselves the ambitious goal of having a net positive impact on biodiversity by 2030. This commitment has been strengthened through our Biodiversity Plan 2030, which establishes the mechanisms to achieve this goal and drive the transformation towards an energy model in harmony with nature and human beings.
This roadmap addresses the impact on ecosystems and species of the Group's business throughout its life cycle, considering the supply chain and creating economic and social value through ecosystem services. The plan is based on applying the conservation hierarchy principle and implementing mechanisms to identify, quantify and monitor compliance.
The basis for this Plan was the approval in 2007 of our Biodiversity Policy, which is integrated into Iberdrola's Governance and Sustainability System. The Plan is based on years of work in integrating the consideration of biodiversity into strategic planning and corporate decision-making.









