ESG criteria
ESG: Sustainable and responsible investing
Corporate social responsibility
Integrating ESG aspects into a company means recognising the key role of environmental, social and governance issues in long-term value creation. It demonstrates their commitment to generating positive impacts on the environment in which they operate, to sustainable economic growth and to the transition to decarbonised societies. ESG aspects are essential in making more responsible decisions and investments for the planet.
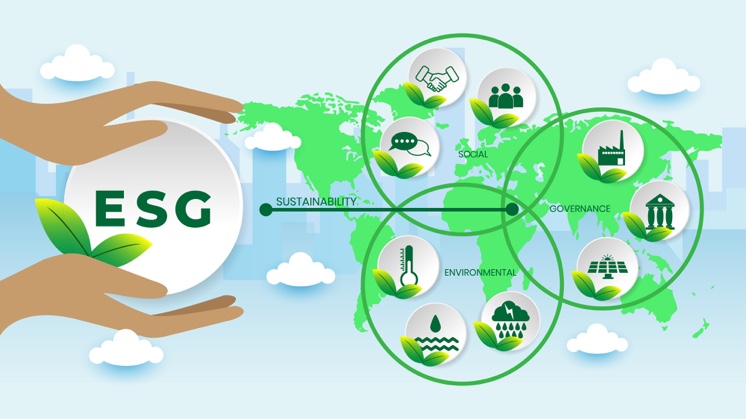
What is ESG
ESG stands for environmental, social and governance, the three most important non-financial factors for a company. It is a strategic and analysis approach that is very widely used by institutional investors and analysts to evaluate sustainability performance. In fact, according to Janus Henderson Investors, a British global asset manager, ESG is today "the bedrock of sustainable and responsible investing for any company". Society and stakeholders are increasingly asking for information on how companies manage issues relating to sustainability.

Corporate purpose and values
A model that prioritizes the people and the planet.

Social dividend
We work to provide shared added sustainable value.

Social contribution
Creating value for society.

Ethics and compliance
Committed to the highest ethical standards.
ESG criteria
Investing sustainably means factoring in aspects other than purely financial ones when making investment decisions, specifically environmental, social and corporate governance factors. With the help of the S&P Dow Jones Indices report Understanding ESG Investing, we will analyse them one by one:
 Environmental
Environmental
Environmental criteria are used to analyse a company's contribution and performance with regard to environmental challenges, such as greenhouse gas emissions, protecting biodiversity, water resources and deforestation. In other words, metrics are used to evaluate companies' environmental impacts and their efforts to reduce them.
 Social
Social
Social criteria are used to evaluate companies' relationship with their social environment (employees, local communities and people in general), considering aspects like employment, health, safety and diversity. They reflect, to a large extent, the company's corporate values and strengthen existing links with communities.
 Corporate governance
Corporate governance
Governance criteria are related to companies' governance mechanisms, shareholder rights and executive management responsibilities. They are used to examine companies' decision-making processes, their organisational structure, control mechanisms and compliance systems, among other aspects.
ESG meaning
A management approach that integrates CSR is a distinct way of running a business because it aims to generate shared value for all stakeholders, and this value must take the sustainability of business models into account. The current context, with climate change as the main challenge, makes this approach more necessary then ever. The concept of ESG renews and updates the concept of CSR and organises the most relevant factors into three areas, establishing a series of criteria that define what sustainable and responsible investment is.
The most widely held view of the importance of ESG factors is that companies are more likely to be successful and generate excellent profitability if they create value for all of their stakeholders. "A well run and responsible company that makes an effort for its employees, customers and the environment we believe, is more likely to exhibit a greater level of resilience and outperform its peers than one that does not. ESG analysis can provide valuable insights about factors that can have a significant impact on the financial metrics of a company and therefore better inform our investment decisions," say Janus Henderson Investors.
What is Socially Responsible Investing (SRI)
A type of investment that uses ESG criteria to select financial assets to invest in. Motives vary from commitment to promoting certain social reforms, such as decarbonising the economy and diversity and inclusion, to the belief that a company with good ESG performance will offer better long-term profitability. In other words, it is an investment that contributes to sustainable development, first defined in 1987 in the context of the UN as "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
What are the ESG principles?
Environmental
- Decarbonisation
- Preserving biodiversity
- Circular economy
- Efficient use of resources
- Innovation

Social
- Diversity and inclusion
- Health and safety
- Training and development
- Commitment to the customer
- Responsible supply chain
- Human rights
- Community development

Governance
- Corporate governance system
- Cybersecurity and data privacy
- Ethics and integrity
- Fiscal responsibility

Sustainable finance

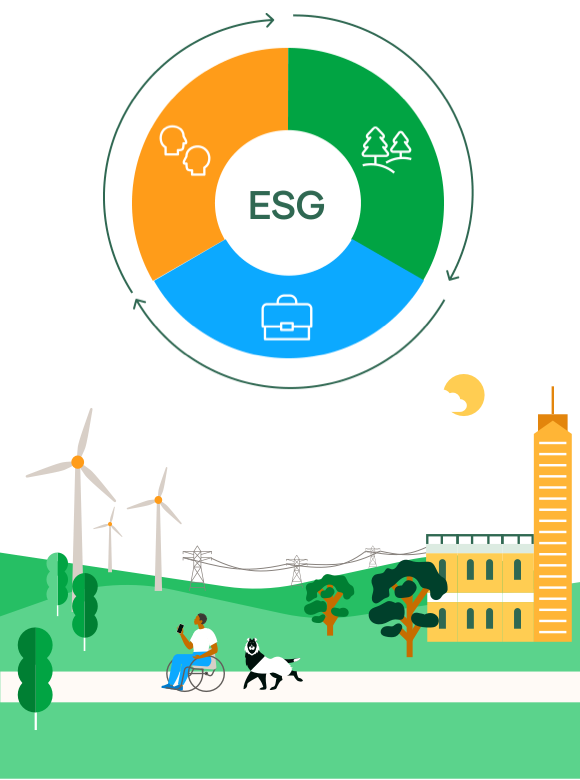
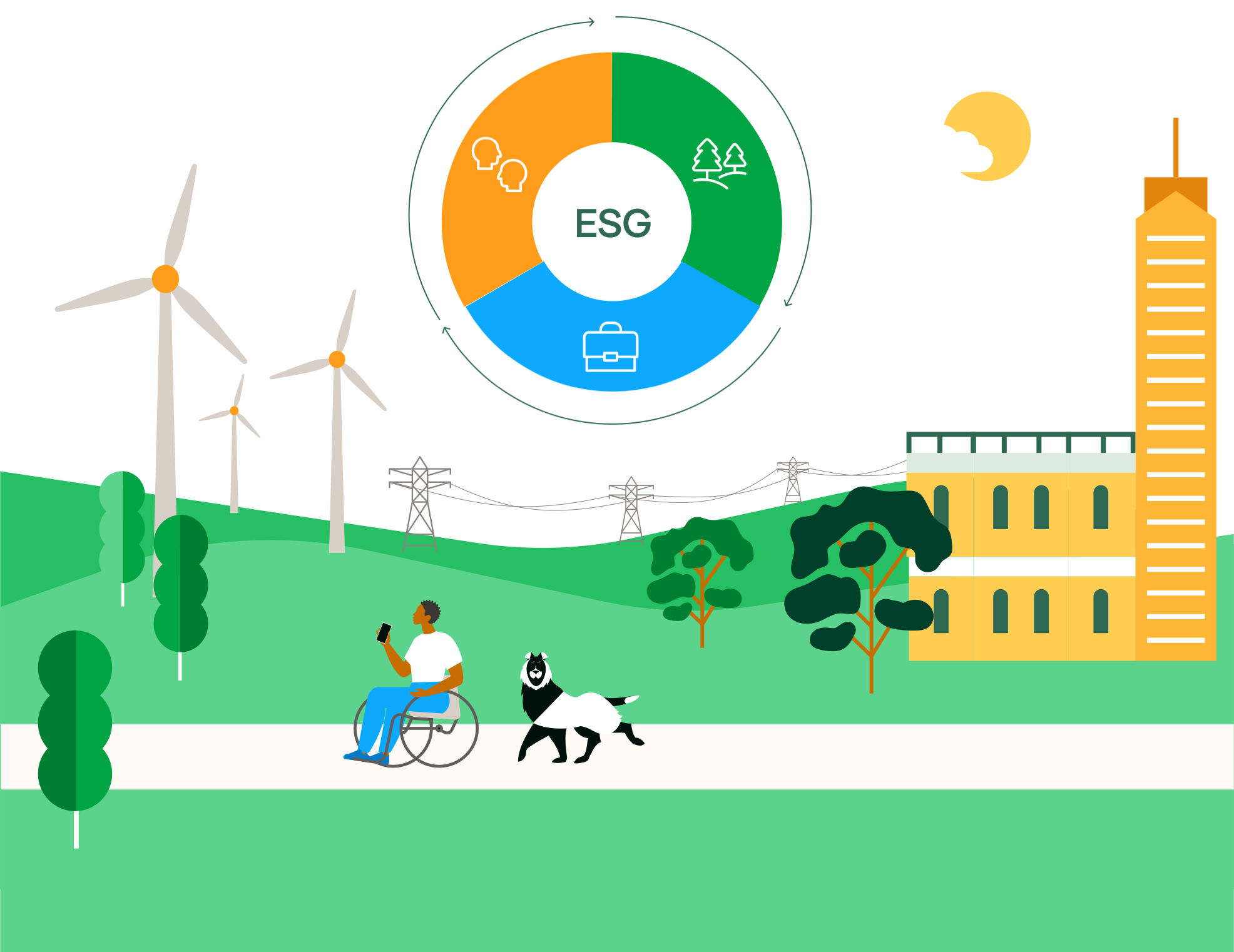
 SEE INFOGRAPHIC: What are ESG principles? [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: What are ESG principles? [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
ESG+F
Due to the increasing focus on integrating sustainability and financial performance, the need for a framework that combines both aspects arises. Therefore, the ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) framework incorporates a fourth component − Finance. The acronym ESG+F emphasises the importance of financial assessment alongside the traditional ESG criteria.
This adds an economic dimension to the analysis by also assessing the companies’ financial health, their profitability, management of economic resources and ability to generate long-term value. It is a criterion that helps to identify companies that are not only sustainable and responsible, but also financially sound.
The opportunities that ESG investments offer
In 2008, the World Bank issued the first ever green bond. Fifteen years later, in 2023, this instrument mobilised over $42 billion for around 690 projects focused on renewable energies and energy efficiency, sustainable mobility, sustainable agriculture and use of land, forests and ecological resources, water supplies and wastewater management, sustainable infrastructure, and management of solid waste, including technological waste. And it continues to grow, because socially responsible investment is an unstoppable trend, which translates into enormous opportunities for the planet:
-
It combats climate change by reducing companies' carbon footprints and encouraging better use of natural resources.
-
It stimulates research by funding projects that result in social good, such as research into cancer or supporting vulnerable groups.
-
It encourages the development of new technologies that have a positive impact on society, such as those that allow the construction of more sustainable buildings or smart networks.
-
It promotes social improvements related to education, health, equality, integration and diversity.




