Artificial intelligence in electricity networks
Artificial intelligence in electricity networks: what does it mean for you?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the electricity sector, making networks more efficient, secure and sustainable. Thanks to AI, companies can anticipate issues, optimise resource use and ensure that electricity reaches your home or business more reliably and at a lower cost. AI is also a key tool in the global fight against climate change. It can make a significant contribution both to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and to adapting to the impacts of climate change. By optimising electricity systems, improving energy efficiency and enabling large-scale integration of renewable energy, AI directly supports economic development.

How does AI improve the efficiency and management of electricity networks?
Artificial intelligence is gaining an increasingly prominent role in the electricity networks sector and is becoming essential for companies looking to improve the service they offer their customers. A wide range of AI-based solutions can be used during the planning, construction, operation and maintenance of power lines, substations, transformer centres and other infrastructure.
What’s more, the development of intelligent virtual assistants is being accelerated, helping resolve enquiries more quickly and streamline claims management, leading to more efficient and personalised customer service.
One of its main advantages is the ability to analyse vast amounts of data in real time, allowing companies to manage their networks more intelligently. For you, this means fewer interruptions, faster responses to incidents and a better match between the network and your energy needs.
AI can also strengthen the resilience of electricity networks to extreme events linked to climate change such as storms, heatwaves or flooding. Advanced algorithms can anticipate risks, optimise emergency response and prioritise investment in critical infrastructure, helping build a safer electricity network that is better prepared for the challenges of the 21st century.
Operational efficiency achieved through AI also helps reduce costs. According to the International Energy Agency (Energy and AI, 2025), the use of AI could unlock up to 175 GW of existing transmission capacity, reducing the need for new infrastructure investment and ultimately contributing to lower tariffs for customers.
What are the key applications of AI in electricity networks?
How are drones, satellites, and LIDAR technology used to monitor energy infrastructure with AI?
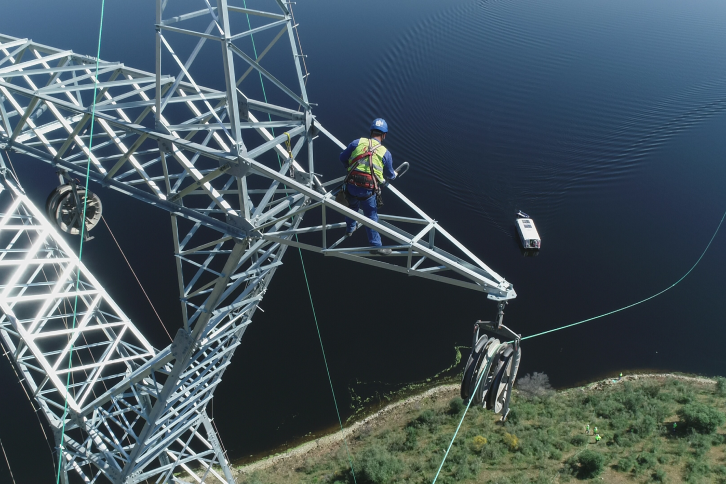
The digital revolution is helping electricity networks become more connected and reliable, but it has also enabled the emergence of devices that can interact with electrical systems in ways that were not previously possible. For example, this is the case with drones, unmanned aerial vehicles that have become essential tools for certain tasks.
Thanks to their versatility, drones represent a major opportunity for network operators, as electricity infrastructure often runs through areas with challenging terrain. These small aircraft, combined with artificial intelligence, enhance the safety of preventive maintenance work, reduce costs and avoid the need for service interruptions by replacing inspection procedures traditionally carried out by people.
LiDAR technology (Light Detection and Ranging) is another tool that supports companies in tasks related to electricity networks. By emitting laser pulses over a surface, this data system can create 3D models of all distribution and transmission lines and their surrounding environment.
This significantly increases knowledge of the network, helping optimise management activities such as inspection, maintenance, repair or replacement.

Flexibility of electricity markets
The keys to ensuring a flexible energy system.

History of artificial intelligence
Discover the almost century-old ideas behind artificial intelligence.

Innovation in networks
We work to improve customer service by enhancing the smart network model.
How does AI improve energy sustainability and support electrification?
Artificial intelligence plays a decisive role in making electricity networks more sustainable, as it enables power to be supplied to more people without the need to build new infrastructure. For example, advanced analysis of electrical and meteorological data makes it possible to expand the technical limits of existing lines and supply more customers within the same network area.
AI can also support access to clean energy in regions with limited infrastructure. By analysing satellite imagery and sensor data, AI algorithms help identify priority areas for electrification and design microgrids tailored to local needs, driving sustainable development and reducing energy poverty.
This not only reduces environmental impact by avoiding the construction of new facilities but also accelerates the transition to a more electrified economy that is less dependent on fossil fuels. As a customer, you benefit directly from a more stable, efficient and environmentally responsible network that is better equipped to meet your present and future needs.
Electricity networks based on smart technologies are the pathway to accelerating electrification.
The Global Smart Grids Innovation Hub: a leading centre for AI and electricity networks
Iberdrola is collaborating with a wide range of AI and technology start-ups through different open innovation initiatives, such as the Global Smart Grids Innovation Hub, which acts as a major ecosystem focused on developing technology that helps the Spanish electricity system remain one of the most advanced in Europe and the world.
Located in Bilbao, the centre promotes disruptive projects that combine AI, big data, cloud computing and other technologies to improve network management. Some of the projects currently underway include:
What are the main technological and operational barriers to implementing AI in electricity networks?
Unlocking the full potential of artificial intelligence requires overcoming several technical and operational challenges. The most significant are:
- Data privacy: training AI models requires large-scale processing of information that, in some cases, may be sensitive or confidential. This raises challenges linked to the protection of personal data, which means that systems must adopt cybersecurity measures that safeguard this information.
- Data availability: for AI algorithms to work effectively, they need large volumes of data, which is not always guaranteed. In addition, many transmission network systems still lack the infrastructure needed to store these data.
- Shortage of professionals and new expertise: there is still a lack of talent specialised in artificial intelligence to meet the sector’s needs. To address this, it is necessary to promote training programmes that develop the required technical skills. It is also important to create groups that foster research into AI in the energy sector, as is the case of Iberdrola’s Artificial Intelligence Centre of Excellence located in San Agustín del Guadalix (Madrid).