Industrial metaverse: merging virtual reality and energy with Iberdrola
Delve into the Industrial Metaverse with Iberdrola
Since the successive strategic announcements by Meta, Facebook's parent company, the metaverse has been at the forefront of the tech scene as a shared virtual environment that proposes a new way of interacting with people. But this concept is not only limited to the social or entertainment sphere, but also extends to transformative applications in industry, giving shape to what is known as the industrial metaverse.
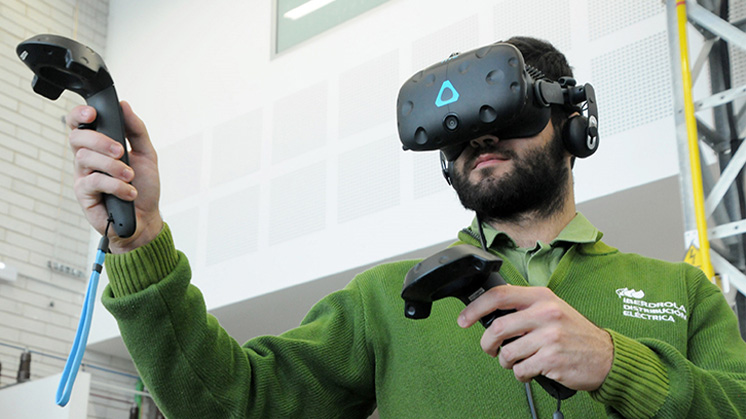

The concept of the industrial metaverse is taking shape as one of the most revolutionary facets of digital transformation in business in general. The emergence of the metaverse as one of the technological trends of this century has brought a new concept into our lives that also extends to the industrial world – where the industrial metaverse emerges as a disruptive and visionary option.
This virtual reality translates into transformative potential for industry. The convergence of technologies such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of digital twins and virtual environments that replicate and simulate complex industrial processes. In the following, we will delve a little deeper into this concept that is presented as a powerful tool to improve the productivity of industries in the digital era.
What is the industrial metaverse?
The industrial metaverse is a concept that connects the virtual world with the physical reality of industry. It represents an extended reality environment, with immersive three-dimensional spaces where companies can interact, collaborate and operate in a wide variety of industry sectors. It is a technology similar to that used in video games, with which it shares technical solutions, and which, together with sensorisation and real-time data, makes it possible to bring a faithful representation of reality to any compatible device – avoiding displacement, improving decision-making and allowing simulations that would be difficult to carry out in the real world.
These are environments that operate through the simulation of real-world elements, such as machines, factories, buildings, networks, transport systems and even entire cities. In this digital scenario, an infinite number of people and assets can interact, breaking down the barriers of distance by enabling individuals from different countries or continents to work together, creating a fully collaborative space.
However, despite having very similar concepts, the industrial metaverse differs from traditional virtual worlds. This space is designed specifically for industrial applications, such as product design, automation, maintenance, data management and process safety – providing truly immersive solutions that offer a number of advantages to its users.
Industrial metaverses are a modern way of representing digital information in an accessible way within a virtual environment. Digital twins display within a virtual representation of a system all the information that is collected in real time from sensors; thus creating an exact replica of the real system, but on which simulations or tests can be performed in dangerous scensarios, but avoiding risks.
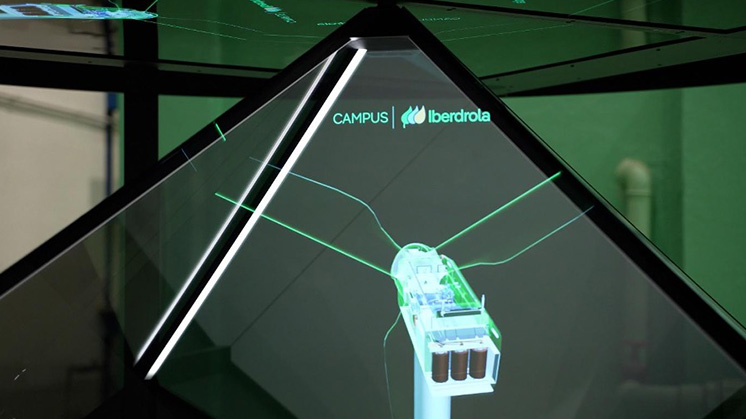
With a digital twin as a base, the industrial metaverse is able to recreate virtual representations of the real world.
Advantages of the industrial metaverse
The application of the metaverse in the industrial world brings a number of significant advantages for companies. Here are some of them:
- Process optimisation: enables simulation and optimisation of processes, which offers greater operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Remote management: facilitates remote monitoring and management of assets and systems, reducing the need to be physically present on site.
- Risk reduction: it allows the identification of potential problems or risks in a preventive way. This reduces the likelihood of incidents caused by these problems and improves safety in the workplace.
- Global collaboration: facilitates collaboration between geographically distributed teams by providing a shared virtual environment to work together.
- Training and education: offers more immersive, realistic and effective training and education opportunities, especially in industries where training is crucial.
- Increased productivity: by reducing downtime, optimising production and streamlining processes, the use of the industrial metaverse ecosystem increases overall business productivity by improving decision-making capabilities.

What is the metaverse?
Learn more about its applications, evolution and the companies behind it.

Virtual Reality, the technology of the future
Virtual Reality is here to stay. But what is it exactly?

What is Augmented Reality?
Nowadays, Augmented Reality is applicable to almost every industry.
Applications of the industrial metaverse
According to studies by Deloitte, applications of the industrial metaverse could be divided into up to four different ecosystems: production (sensing and detection, factory asset intelligence and product development), supply chain (supply network mapping, digital warehousing and control towers), customer (after-sales services and virtual product experiences) and talent (recruitment and training).
In the field of design and engineering, for instance, metaverse is used to create three-dimensional models for simulation and testing of virtual prototypes prior to real-world implementation, such as in the manufacture of cars or aircraft. This uses the same principle as the digital twin, which is able to simulate the same conditions and characteristics as in reality.
In the case of the energy sector, the industrial metaverse enables real-time monitoring of facilities, employee training and other business operations. In logistics, visual environments facilitate supply chain planning and tracking.
Iberdrola, as a company that embraces digitalisation as an important part of its business, also uses disruptive tools to boost its projects, in addition to signing collaborations in the search for new technological solutions. A clear example is the joint project that Iberdrola España has launched with the Gipuzkoan start-up Multiverse Computing, in which the companies will work together to develop quantum computing solutions for the electricity grid.
As for the industrial metaverse created by Iberdrola, the company defines as its main objective to unite the real and virtual worlds to optimise its operations. In the field of smart grids – one of its application areas – employees use it to prepare jobs in a virtual environment from the office, allowing them to configure locations and identify real risks.
Subsequently, workers in the field can visualise this preparation using Mixed Reality, which incorporates a virtual layer to the physical reality to increase understanding of the environment and safety. This technology also offers real-time assistance from the office, where virtual reality allows interaction with the representation of reality that the on-site worker is seeing.
The suppliers emphasise that this Iberdrola solution is highly advanced and a concrete example of how the metaverse can be applied to an industrial or business environment. Furthermore, they state that the company's industrial metaverse enriches in-office work with resources that were previously limited to physical presence, while improving efficiency and safety on-site.
 SEE INFOGRAPHIC: What activities can be carried out in the industrial metaverse? [PDF]
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: What activities can be carried out in the industrial metaverse? [PDF]
Digital twins: technologies of the industrial metaverse
Digital twins are virtual representations of a real-world target, system or product. These digital recreations – which can be of an aircraft turbine, wind turbine blades or a robot handling industrial tasks – are created using real-time data that can be captured by sensors and blended with predictive models based on Big Data, allowing companies to simulate and better understand the performance and behaviour of their assets.
In the context of the industrial metaverse, digital twins play a key role in providing connectivity and advanced analytics to the physical infrastructure under study. They are mainly used to optimise asset and process management. So increasingly, large industrial companies are being forced to integrate digital twins into their production chains in the interest of better market competitiveness.
In a smart factory, for instance, originated in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a digital twin of a machine makes it possible to monitor its condition in real time, anticipate potential problems and schedule preventive maintenance. This reduces downtime and increases operational efficiency. Furthermore, in logistics, warehouse digital twins can help optimise distribution and product flow; thus improving the supply chain.
Keys to the success of the industrial metaverse
Like any technological trend that is still developing, the industrial metaverse is not without challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its sustainable success in the future. One of the main challenges is cybersecurity, as the convergence of virtual systems and the real world opens new doors for potential cyber attacks. Thus, it is key for companies to ensure the protection of critical data for the proper use of the metaverse.
In order for it to be widely adopted, massive investment in technological infrastructure and adequate training of the workers who will use this digital ecosystem will also be essential. At Iberdrola, for example, we intend to exceed 4,000 million euros of investment in Innovation, Development and Research (R&D&I) activities by 2030, allocating resources to the development of digitisation and artificial intelligence systems, as is the case of the industrial metaverse.
Finally, it is important to address ethical and privacy concerns related to data collection, and this relies heavily on the creation of appropriate regulatory frameworks. This set of rules are key to ensuring that the industrial metaverse is developed and employed in the safest possible way.





