eHealth
eHealth, when technology becomes the key to social well-being
During the coronavirus crisis, some countries have leveraged the predictive power of big data to keep the global spread of the pandemic in check. This is just one of many examples of how technology can be wielded under the banner of eHealth to help care for and save millions of people around the world.

Today we live longer than yesterday but less than tomorrow. Since 1960, World Bank data tells us that life expectancy has risen by 20 years, and who knows if soon we could live to be 150? According to Gregory Stock, biophysicist and former director of the Program on Medicine, Technology and Society at the UCLA (University of California), it could well happen. What we all know for sure is that if people are to live longer and better, we will have to rely on research and technology, the same combination that has managed to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is eHealth?
The healthcare sector has been flung into a digital revolution, with technology working its way into every process. The concept of digital health or eHealth emerged to designate the use of ICTs in the healthcare sector, equipping it with cutting-edge resources to ensure more efficient management and optimised diagnosis, definitely, a better patient care. This includes innovations in a whole host of areas such as doctor-patient communication, research and hospital management.
The eHealth industry is on the rise. In 2018, it saw global investments of $14.6 billion according to the Statista data portal, which means 1200 % more than in 2010. Interest in eHealth has risen among countries belonging to the World Health Organisation (WHO), with 58 % having implemented specific strategies to digitise health.
Digital health services
Another of the great advantages of new technologies in the healthcare sector is how versatile they are. Here are some of the most widespread solutions they offer:
-
Telehealth. Providing care at a distance means people in remote areas with limited access to healthcare can get the medical attention they need. It also saves time, money and travel for both doctors and patients.
-
Apps. Having mobile apps dedicated to health turns our smartphones into personal trainers, sleep monitors, diagnostic, devices and more, with apps for both healthcare professionals and patients.
-
Serious Games. These special video games are used as a learning resource for healthcare professionals and students to enhance their training. They can also be used by people wishing to learn more about specific pathologies.
-
Wearable technology. The well-known term wearables, includes smart clothing and accessories such as wristbands, glasses and watches to monitor and collect information on our health and physical condition.
-
Augmented reality. AR can help health professionals to visualise organs in 3D, for example, or check a patient's record in real time. It can even be used in surgical procedures with special AR headsets.
-
eHealth record. Having a digital health record means information can be stored in one place but be available anywhere, so patients can share it safely and healthcare staff can access it at any time.
Advantages and benefits of eHealth
Thanks to services like these, digital health enables us to apply new methods, means, tools and channels that lead to a series of benefits:
Improved patient monitoring
Communication is easier with this new digital channel, helping to bridge the gap between doctors and patients. Technology also means the patient's condition can be monitored and their progress can be recorded in real time.
More informed patients
As patients, we can make better health decisions when we understand them and have the power to manage their own health. ICTs also provide us with access to guide books and best practice, something very useful, for instance, during the pandemic if they come from reliable sources.
Encouraging healthier habits
New technologies are changing the way we look after ourselves with apps and devices that keep track of what we eat, how much exercise we do, how long or soundly we sleep and how fast our heart rate is.
Easier decision-making for healthcare staff
eHealth is also transforming the way professionals deal with disease. ICTs can help, for instance, to identify optimal treatments more easily or detect illnesses at an early stage.
More accessible and equal healthcare
Access to healthcare is no longer limited by time and space, which means avoiding unnecessary travel. Moreover, technology brings healthcare to more people, especially patients at risk of exclusion, which means more equal opportunities for everyone.
More efficient hospitals and health clinics
Connected facilities mean a streamlined health system, minimise the chance of human error and cutting costs. In addition, techniques such as big data, processes are being automated.
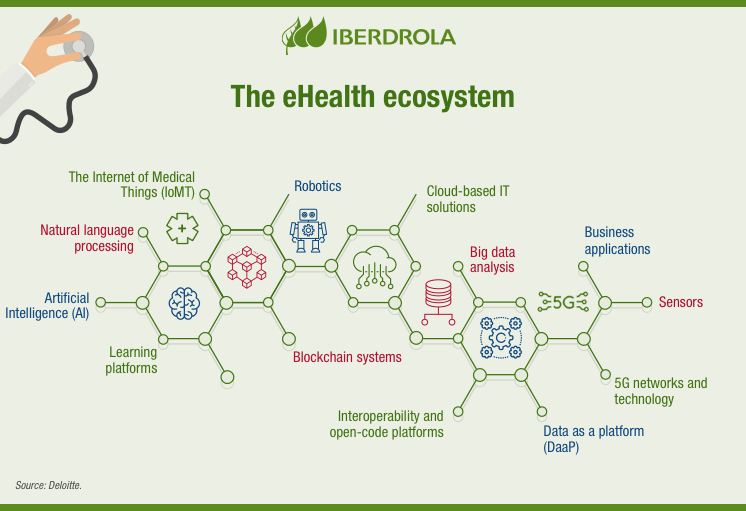
New technologies in health
Digitising health involves using new technology. Here is some of them and their specific uses:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things helps to customise healthcare, save costs, reduce the likelihood of incorrect diagnosis and shorten waiting times. The connection between the physical and digital world will be crucial in equipment such as inhalers and audiometers.
- Big data
Using big data to perform macro data analysis allows for tailored treatments and helps to detect the risk factors and potential side effects of drugs. The insight gained from it has proven critical in understanding and containing the spread of COVID-19.
- Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can help healthcare professionals to make wiser decisions and deliver better treatments. During the coronavirus crisis, AI was used to identify the sequence of antibodies and its compatibility with future treatments.
- Blockchain
Blockchain affords safe access to a patient's health record, which makes a more efficient administration. It also allows pharmaceutical labs to keep a more precise record in the drug production process.
- 3D and 4D printing
The use of 4D printing in ultrasound scans, for example, gives us more precise insight into the structural and functional development of the nervous system of the foetus. Furthermore, the shortage of safety equipment during the coronavirus crisis led to the production of medical items using 3D printers.
- Chatbots
Chatbots provide a tool to enable faster and more direct doctor-patient communication. The World Health Organisation set up one of these channels during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Virtual reality
Some of the most significant contributions that VR technology can make include assisting with patient rehabilitation and treating psychological disorders.




